Choosing the right method
The answer varies case-to-case, but we'll touch a bit on how to think about this.
Who is the output for?
If the LLM output is meant to be consumed by the machine, which is mostly the case, constrained decoding is the way to go. It guarantees 100% schema adherence.
Unconstrained methods show varying error rates based on schema and setup. If the LLM output is meant to be consumed by a human and only needs to loosely adhere to schema, it is worth trying them. They are easy to setup, and may even produce slightly better outputs.
Time-per-output-token
If you need high throughput or large volumes of outputs, time-per-output-token matters more than anything else. Constrained decoding is slightly faster in most cases.
This might be counterintuitive as it adds an extra computation step for token masking. But we need to remember that unconstrained outputs occasionally fail and need regeneration, which increases latency linearly with the error rate.
Early implementations of constrained decoding did not create token masks fast enough to match the speed of output generation, which introduced lag and GPU costs. This is solved now, and implementations match or even surpass time-per-output-token of raw sampling.
Time-to-first-token
Constrained decoding prepares for token masking before it starts to generate output. This can increase time-to-first-token anywhere between milliseconds to seconds, depending on schema complexity. Unconstrained methods don't incur this cost.
This is a one-time cost incurred when you use a schema to generate outputs for the first time, after which the cost is amortized when you use the same schema across many generations.
Time-to-first-token becomes relevant only when you generate dynamic schemas on-the-fly. In such cases, use constrained decoding optimized for TTFT, or unconstrained methods.
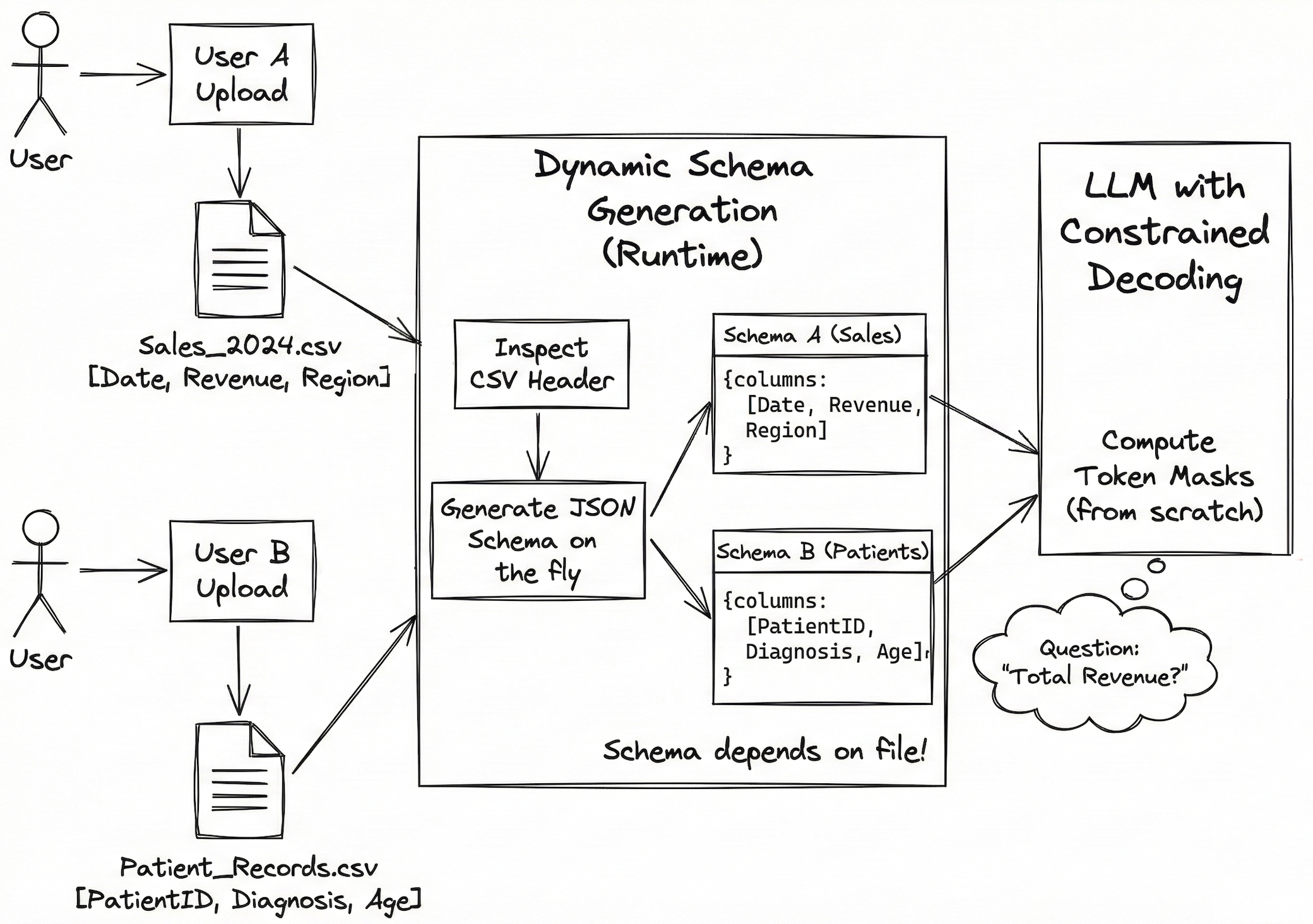
Output quality within schema
Whenever we mask the "most likely" tokens, we derail the LLM from its natural path and the patterns it has learned. LLMs are known to produce low quality outputs on unnatural paths.
Constrained decoding can degrade output quality for deep reasoning tasks. If you observe this, a better approach is to use CoT / hybrid constrained decoding or unconstrained methods. We'll discuss them shortly.
GPU Costs
Cost is tied to GPU time, which depends on your specific time-to-first-token and time-per-output-token. Constrained decoding comes out cheaper in most situations.
Unstructured methods can come out cheaper in some rare cases, if they have achieve high schema adherence on their own, or if schemas are highly dynamic and complex.
Open-source vs closed
Constrained decoding requires access to the model's logits to mask invalid tokens. This is standard in open-source hosting.
But closed providers (OpenAI, Gemini, Claude) offer this as a server-side feature. You don't have access to the logits, but the provider implements constrained decoding on their end. This limits capabilities and optimizations, adds costs you pay to the provider, and doesn't allow custom logic.
Still, it is a convenient way to get structured outputs from the best available commercial models, and can make sense if you don't need high throughput, large output volumes, or complex logic.