Outlines-core
Outlines-core, maintained by .txt, was the first backend optimized enough to support production-grade structured outputs. It takes regex input and converts it into an FSM.
Outlines-core implements two major optimizations to make it fast:
-
It pre-computes the entire FSM. In each token generation step, it only needs to lookup the valid tokens in O(1) time. This prevents any lag in token masking.
-
It deduplicates deterministic FSM paths.
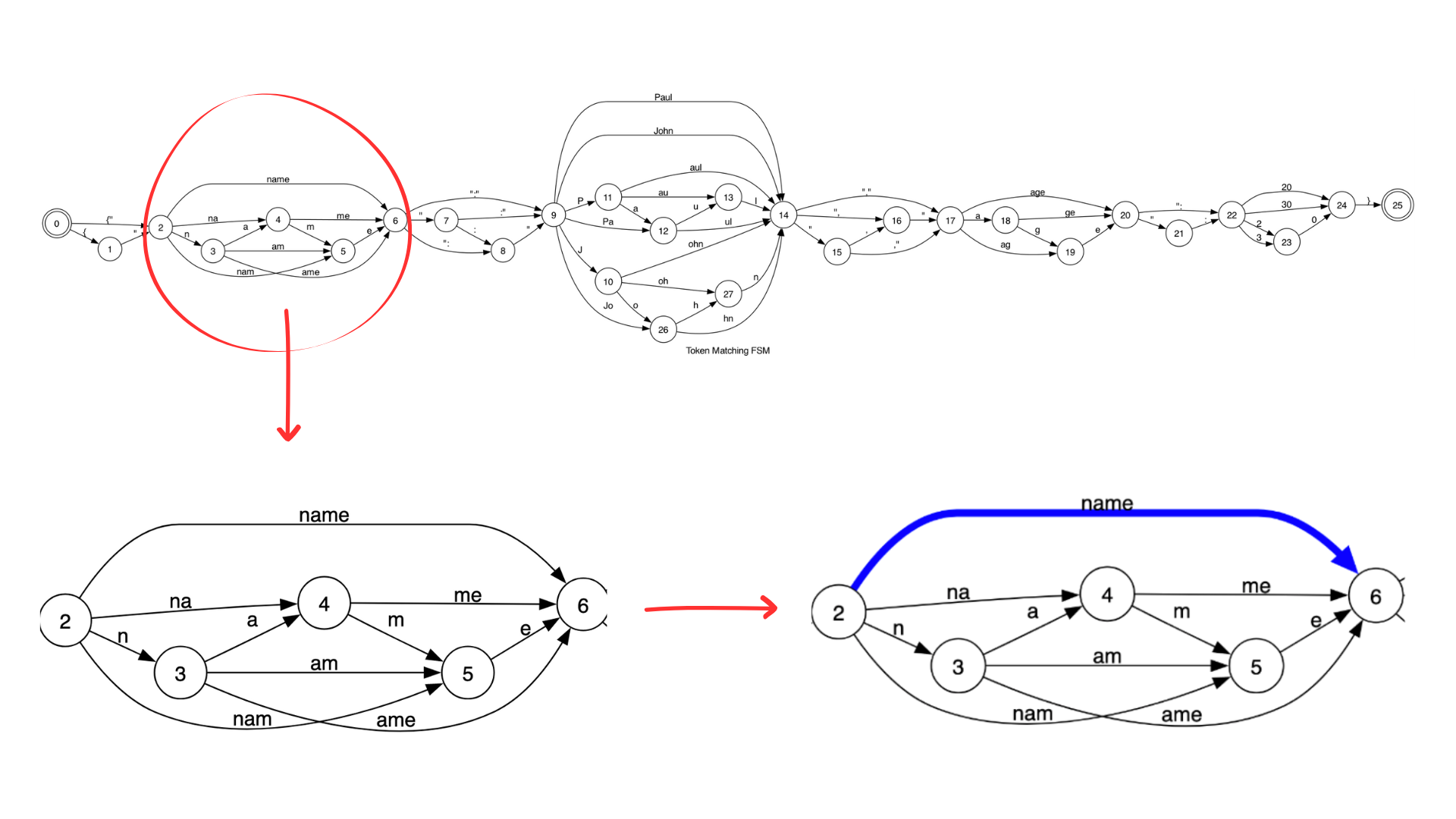
There are 7 paths from State 2 → State 6, but all of them generate name. Outlines-core uses algorithms to pick one path and prune others. It saves the cost and inference time of multiple LLM calls at runtime.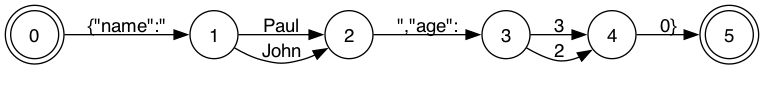
The condensed FSM needs only 2 LLM calls, at State 1 and State 3, where we actually need the LLM to generate output values within the schema.
Limitations
-
Outlines-core does not support PDAs, and by extension, large / infinite / recursive schema.
-
Even with a fixed depth limit, schemas that allow nested operations like
(A AND (B OR C)), or knowledge graph schemas, create massive FSMs. It is more performant to use a backend that supports CFGs. -
Time-per-output-token and time-to-first-token are higher in Outlines-core compared to newer backends that have optimized token masking for high-performance systems and complex schemas. They also have better integrations with high-performance inference engines like SGLang, vLLM, etc.
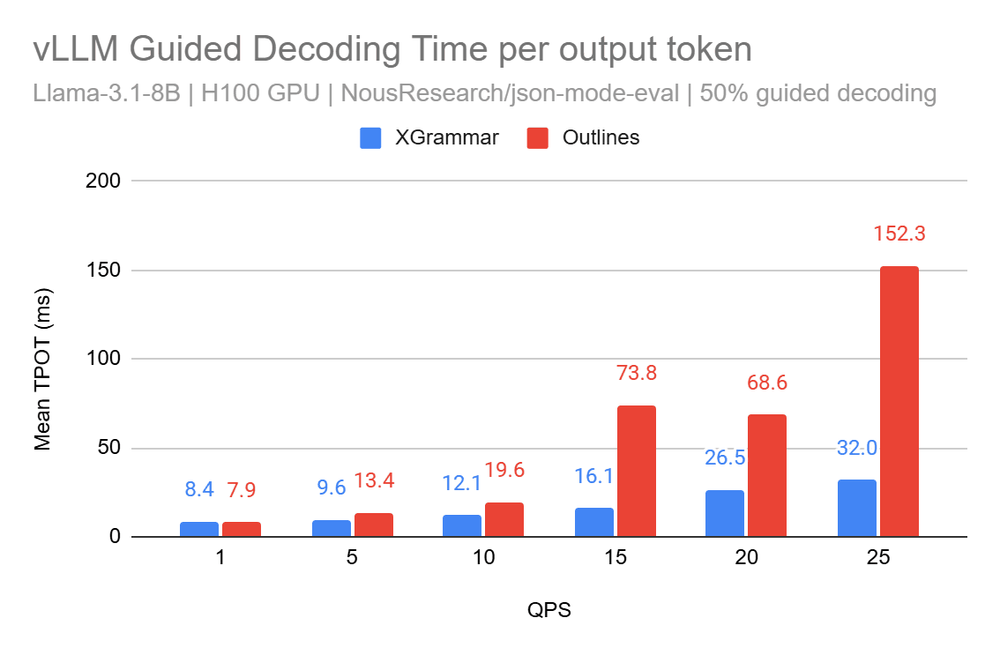
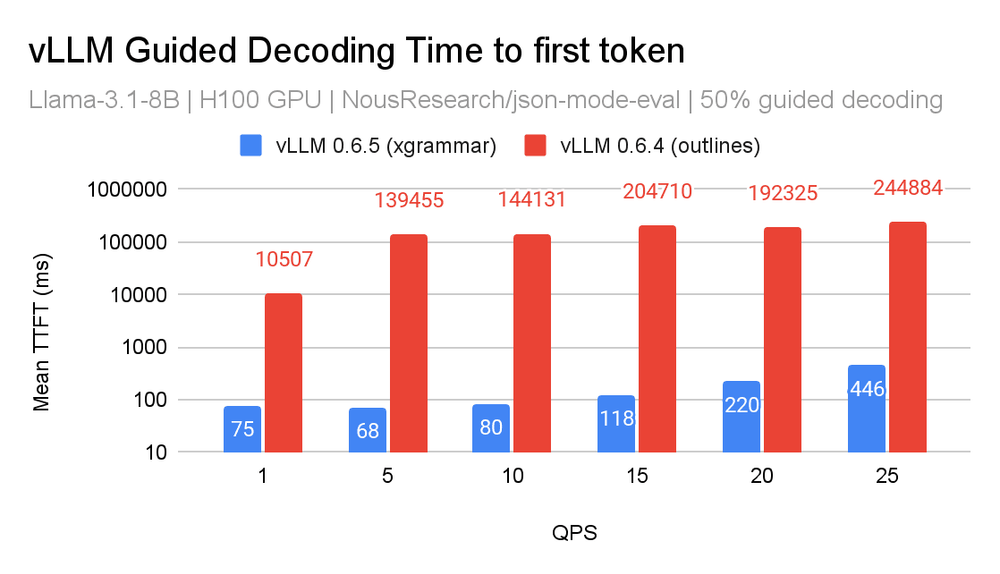
Outlines-core is slower per output token compared to newer backends. -
Pre-computing the FSM delays time-to-first-token. This cost is amortized when you use the same schema across generations, but becomes a problem in dynamic schemas as you incur TTFT costs with every new schema.
-
Avoid using it for interleaved flows (prompt → output → prompt → output...). llguidance is undisputedly the best option for these flows.
llguidance and XGrammar generally work better in high-performance production systems, both for recursive and non-recursive schema.
When to use it?
-
Use in production systems with low-to-medium throughput needs and simple schemas. Outlines Python library, built on top of Outlines-core by the same team, can get you 80% of the performance with 20% of the setup pain. It is also great for prototyping, POCs, internal tools, and one-time tasks.
-
Outlines-core might be a good option if you want a small dependency surface for building your own inference stack, or a plugin inside another system. Outlines-core is lightweight and portable, with a Rust core and bindings potential beyond Python.