The recruitment process is a labyrinth of steps, each crucial to ensuring the best talent comes onboard. As the integration of technology into recruitment has expanded, it's worth pausing and asking: Is it speeding up the process or complicating it further? Let’s dive in.
1. The Workflow Needed to Hire a Candidate
From the moment a vacancy is identified to the point where a new employee is integrated into an organization, there are multiple phases. The journey begins with a job posting and subsequently moves through application collection, screening, interviewing, offer negotiation, and finally onboarding. Each phase is essential and calls upon specific tools, software, and stakeholders to ensure its success.
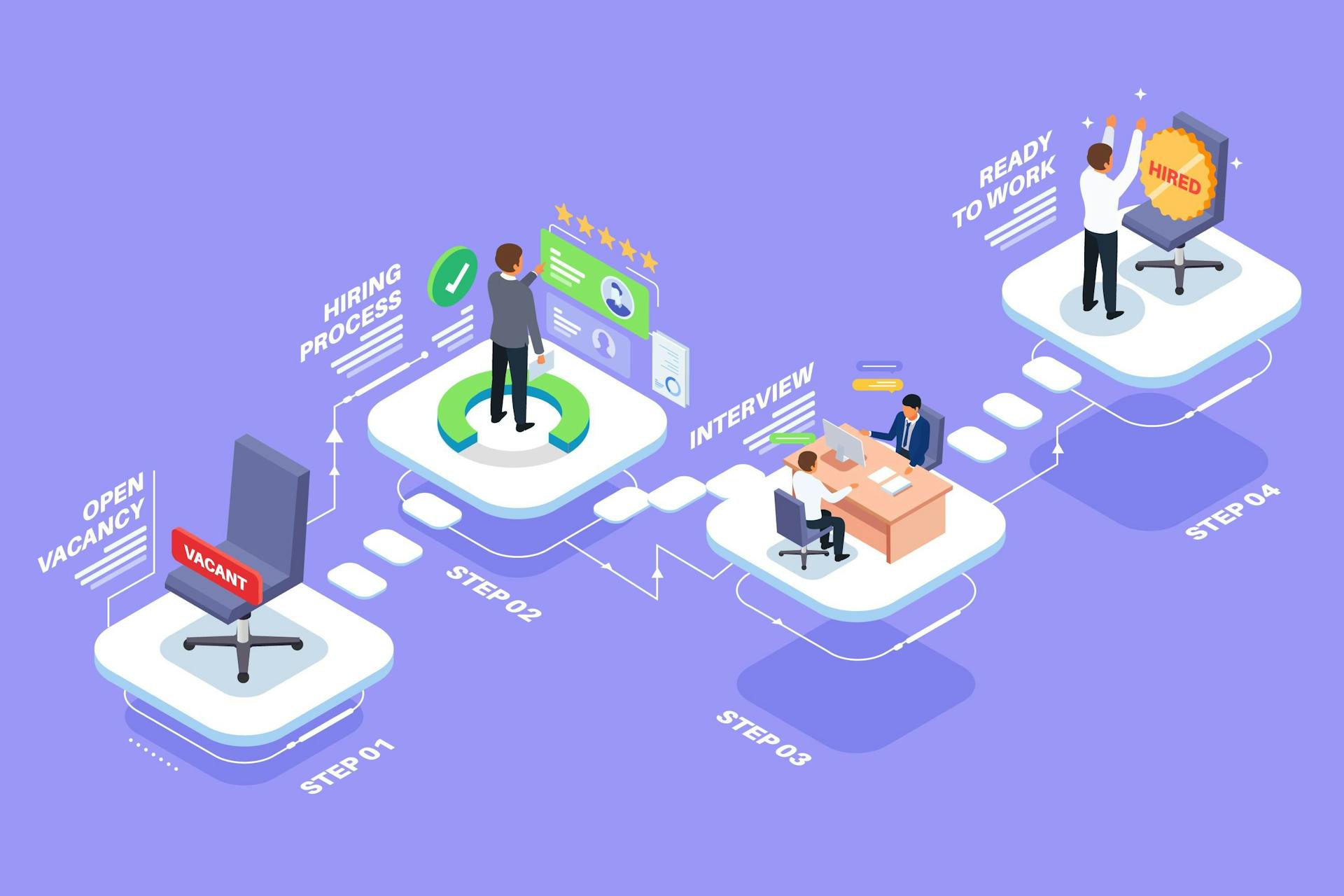
2. Different Technology and Software Used
Technology is deeply entrenched in recruitment. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) such as Greenhouse manage and track candidates. Platforms like Codility are pivotal for skill assessments, and tools like DocuSign have revolutionized contract exchanges, taking them from the desk to the screen. The technological landscape in recruitment is vast and continuously evolving.
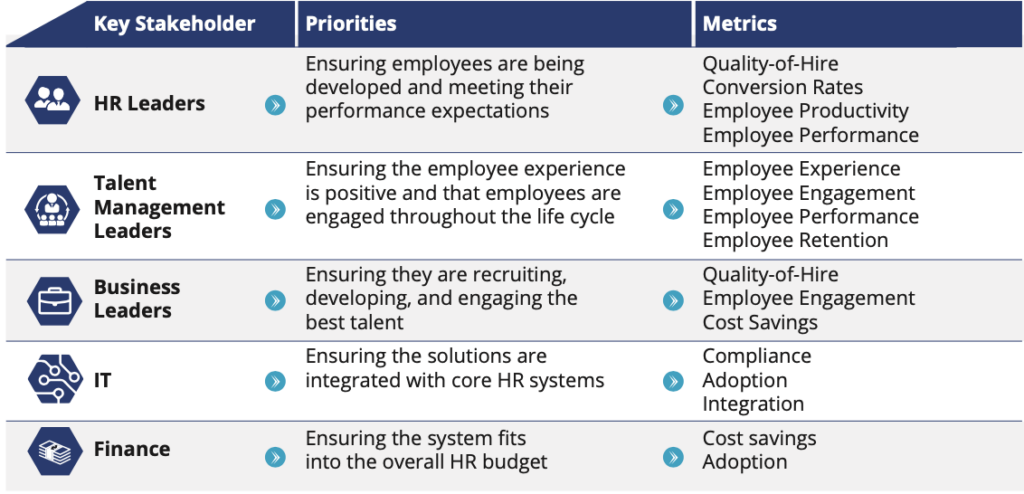
3. Who Are the Different Stakeholders Involved
Beyond the obvious players like HR managers, recruiters, and candidates, the recruitment arena includes department heads, senior management, the IT department, the executive team, legal, and finance. Together, they ensure that the hiring process aligns with company goals, adheres to legalities, and stays within budget.
4. Processes, Workflows, and Software Touchpoints
From sourcing candidates using platforms like LinkedIn and Indeed to onboarding via specialized software, each recruitment phase has its associated processes and technologies:
- Candidate Sourcing:
- Systems: Job Boards, Social Media, Sourcing Tools, ATS.
- Steps: Define role, search candidates, review, and outreach.
- Candidate Screening:
- Systems: ATS, Resume databases.
- Objective: Match candidates to role needs.
- Interview Scheduling:
- Systems: ATS, Calendly, Google Calendar.
- Objective: Smoothly line up candidate interviews.
- Interview Feedback Collection:
- Systems: ATS, Feedback platforms.
- Objective: Gather post-interview insights.
- Offer Management:
- Systems: ATS, HRIS.
- Objective: Seal the deal with the chosen candidate.
- Onboarding:
- Systems: ATS, HRIS, LMS.
- Objective: Integrate the new hire into the organization.
- Background Checks:
- Systems: ATS, Checkr.
- Objective: Verify a candidate's background.
Schedule a free consultation on Recruiting Automation
5. Time, Delays, and Why

While each recruitment phase has its timeline, delays can creep in. Cumbersome applications, poor communication, lengthy decision-making, and complicated offer processes can deter candidates. Here's an illustrative table:
| Step | Approx. Time | Software | Stakeholders | Drop-off % |
| Job Posting | 1-2 days | ATS, Job Boards | HR, Management | 5% |
| Application | Instant to a few days | ATS | Candidates, HR | 10% |
| Screening | 1-2 weeks | ATS, Screening tools | HR, Recruiters | 15% |
| Interviews | 1-3 weeks | Video tools, Calendar tools | Interviewers, Candidates | 20% |
| Offer | 1-2 weeks | ATS, E-signature | Management, HR, Candidates | 5% |
| Onboarding | 1 week to several months | HR Software | HR, IT, New Hires | 5% |
6. Speeding Up via Workflow Optimization

- Automate Where Possible: Look for opportunities to automate repetitive tasks. For example, you can make use of Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) equipped with AI capabilities to screen resumes and save time. Additionally, automation can also be implemented for scheduling interviews and sending automated responses to candidates, further enhancing the efficiency of the recruitment process.
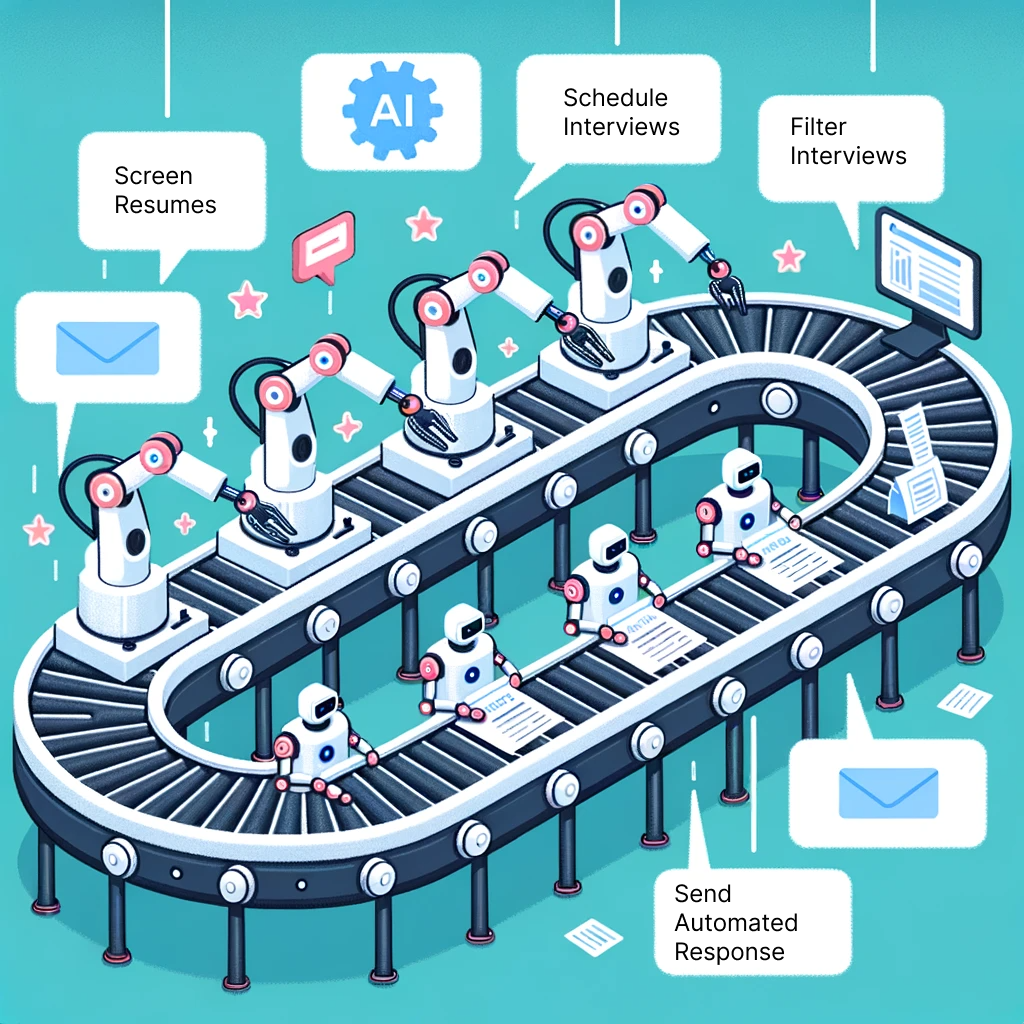
- Synchronize Tools: It is important to ensure that all tools and software used in the recruitment process can integrate and communicate with each other seamlessly. This will help reduce data redundancy and improve efficiency. By synchronizing the ATS with other HR software, such as payroll and employee management systems, the entire employee lifecycle can be streamlined, from recruitment to onboarding and beyond.
- Training: Make sure that all stakeholders involved in the recruitment process receive proper training on how to effectively use the tools and software. This includes recruiters, hiring managers, and even candidates. Providing comprehensive training programs can empower users to leverage the full potential of the software and optimize the recruitment process.
- Feedback Loops: Establish a system to regularly gather feedback from all parties involved in the recruitment process. This feedback can be used to identify areas for improvement and iteratively refine the process. Conducting surveys, holding feedback sessions, and encouraging open communication can foster a culture of continuous improvement and ensure that the recruitment process remains aligned with the evolving needs of the organization.
- Reduce Manual Touchpoints: While human judgment is essential in the recruitment process, it is important to identify any manual interventions that may be slowing down the process unnecessarily. Streamlining these touchpoints can help improve efficiency. For example, replacing manual resume screening with automated algorithms can significantly reduce the time spent on initial candidate evaluation, allowing recruiters to focus on more strategic aspects of the hiring process.
Schedule a free consultation on Recruiting Automation
Automating recruiting process
To automate the recruitment processes mentioned, artificial intelligence (AI) can be utilized in the following ways:
1. Candidate Sourcing:
- AI can analyze job requirements and search criteria to identify potential candidates who match specific role criteria more efficiently.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be employed to interpret unstructured data from various platforms, such as LinkedIn profiles, GitHub repositories, and Twitter bios, to create a unified candidate record in the Applicant Tracking System (ATS).
- Machine Learning (ML) algorithms can predict candidate fit based on historical data and recruiter feedback, improving the accuracy of candidate sourcing.
2. Candidate Screening:
- AI algorithms can automatically screen resumes by extracting structured data like skills, experience, and education, reducing the need for manual evaluation.
- ML models can be trained to identify qualified candidates based on historical screening decisions and feedback, improving screening accuracy.

3. Interview Scheduling:
- AI-powered scheduling tools can analyze candidate and interviewer availability, preferences, and constraints to automatically schedule interviews, eliminating the need for manual coordination.
- Chatbots can be used to interact with candidates and schedule interviews based on their availability, providing a seamless and efficient experience.
4. Interview Feedback Collection:
- AI can assist in analyzing interview feedback by extracting key insights and identifying patterns, helping recruiters make more informed decisions.
- NLP techniques can be applied to interpret and categorize interviewer feedback, reducing the time and effort required for manual analysis.
5. Offer Management:
- AI-powered systems can generate structured offer letter templates based on candidate records, streamlining the offer creation process.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG) techniques can be used to customize offers and negotiate offer terms automatically, improving efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
6. Onboarding:
- AI can streamline the onboarding process by automatically generating training assignments and IT requests based on new hire data.
- Chatbots or virtual assistants can provide automated guidance and support to new hires, answering frequently asked questions and facilitating their integration into the organization.
7. Background Checks:
- AI can assist in evaluating background check results by flagging potential issues for human review, improving the efficiency and accuracy of the process.
By leveraging AI technologies in these areas, organizations can significantly automate and optimize the recruitment process, saving time, reducing errors, and enhancing the overall candidate experience.