The Ultimate Guide to Supply Chain Automation
Supply chains today are very complex, with numerous stakeholders, processes, and data points involved.
From raw material sourcing and production to shipping and delivery, managing the supply chain can be a daunting task for businesses.
This is where supply chain automation comes into play, offering a range of benefits, from increased efficiency and productivity to reduced costs and errors.
In this blog post, we'll discuss the importance of supply chain automation and how Nanonets can help businesses automate their supply chain processes and workflows.
What is Supply Chain Automation?
Supply chain automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks and processes that were traditionally executed manually within the supply chain.
This is not merely a trend but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to remain competitive in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Quick Historical Recap
The evolution of supply chain automation can be traced back to the advent of early computing technologies in the mid-20th century.
- Initially, businesses relied on rudimentary systems for inventory management and order processing.
- The landscape shifted dramatically with the introduction of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems in the 1990s. These systems integrated various business functions, providing a unified platform for managing the supply chain.
- The advent of the internet and subsequent digital innovations in the early 2000s further propelled supply chain automation. E-commerce giants like Amazon pioneered the use of sophisticated algorithms and robotics to optimize logistics and warehousing.
- Today, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Workflow Automation and the Internet of Things (IoT) represents the cutting edge of supply chain automation, enabling unprecedented levels of efficiency and precision.
Key Components and Technologies Involved
Below are the key components of a modern automated supply chain workflow. We will later explore in detail how they fit in the supply chain workflow and how to implement them.
Optical Character Recognition & Intelligent Document Processing

OCR technology is pivotal in transforming paper-based and digital documents into editable and searchable data. By automating data entry and extraction, OCR minimizes human error and accelerates information processing. This is crucial for handling complex supply chain documents such as invoices, purchase orders, and shipping manifests.
Workflow Automation and Integrations

Workflow automation automates the flow of tasks and information between different apps and databases. This ensures seamless operations and real-time visibility across the supply chain.
Accounts Payable (AP) Automation and Invoice Matching

AP automation streamlines the entire accounts payable process, from invoice receipt to payment.
Firstly, this technology automates invoice capture, approval workflows, and payment processing, significantly reducing processing times and errors.
Secondly, Invoice matching is a critical component of AP automation, which ensures that invoices are accurately matched with purchase orders and receiving documents, preventing discrepancies and fraud.
Thirdly, integrating AP automation with accounting software ensures seamless data flow, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in financial management. This integration eliminates manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors, and provides real-time visibility into financial transactions, enabling better decision-making and financial control.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
.png)
RPA involves the use of software robots to automate repetitive tasks. In supply chain management, RPA can streamline activities such as order processing, inventory tracking, data entry and customer service operations.
Benefits and Challenges
Supply chain automation brings a lot of benefits on the table.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automation significantly reduces the time required to perform routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities. For instance, automated order processing can handle high volumes of transactions swiftly and accurately.
Cost Reduction
By minimizing manual labor and reducing errors, automation lowers operational costs. Moreover, optimized inventory management and improved demand forecasting help reduce holding and stockout costs.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automated systems are less prone to errors compared to manual processes. Technologies like OCR and IDP ensure accurate data capture and processing, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of supply chain operations.
Better Decision-Making through Real-Time Data
Automation provides real-time visibility into supply chain activities, enabling better decision-making. Access to accurate, up-to-date information allows businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and operational issues.
At the same time it is imperative to be cautious and prepared beforehand for challenges that arise during the transition towards automation.
- Initial Investment and ROI: The initial cost of implementing supply chain automation can be substantial. Businesses must carefully evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) and ensure that the benefits outweigh the costs in the long run.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating new automation technologies with legacy systems can be challenging. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure compatibility and avoid disruptions in operations.
- Change Management and Employee Training: Successful automation requires a shift in organizational culture. Employees need to be trained to work with new technologies and processes. Effective change management strategies are essential to manage resistance and ensure a smooth transition.
So while supply chain automation offers transformative potential, it demands careful consideration of both its benefits and challenges. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness. However, thoughtful planning and execution are crucial to realize its full potential and ensure sustainable success.
Checklist to Get Started
Here are some things to consider while getting started with automating your supply chain processes and workflows.
Assessment and Planning
Successful implementation of supply chain automation begins with thorough assessment and planning. This foundational step ensures that the chosen technologies align with the specific needs and goals of the organization.
1. Conducting a Needs Assessment: Begin by analyzing current supply chain processes to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. This involves mapping out existing workflows, gathering input from stakeholders, and reviewing performance metrics.
2. Identifying Automation Opportunities: Based on the needs assessment, pinpoint areas where automation can deliver the most significant impact. Look for repetitive, time-consuming tasks that are prone to errors, such as data entry, order processing, and invoice matching.
3. Setting Clear Objectives and KPIs: Define specific, measurable objectives for the automation initiative. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success. Objectives might include reducing processing times, decreasing error rates, and improving customer satisfaction.
Technology Selection
Selecting the right technology is critical to the success of supply chain automation. This involves evaluating different solutions and vendors to ensure they meet your needs and are scalable for future growth.
4. Evaluating Different Technologies and Vendors: Research and compare various automation technologies and vendors. Consider their features, ease of use, customer support, and track record in the industry. Seek out case studies or testimonials from similar businesses.
5. Considering Scalability and Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen technologies can scale with your business and integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. Scalability is crucial for accommodating future growth and evolving business needs.
6. Pilot Testing and Feedback: Before full-scale implementation, conduct pilot tests of the selected technologies. Gather feedback from users to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine the solution and ensure it meets your requirements.
Integration Strategies
Integrating new automation technologies with existing systems is often one of the most challenging aspects of implementation. Effective integration is essential for maximizing the benefits of automation.
7. Integrating with Existing Systems (ERP, CRM, etc.): Develop a comprehensive integration plan that outlines how the new technologies will interface with existing systems, such as ERP and CRM platforms. Ensure that data flows seamlessly between systems to avoid silos and maintain data integrity.
8. Data Migration and Management: Carefully plan the migration of data from legacy systems to the new automated environment. This involves cleaning and organizing data to ensure accuracy and consistency. Implement robust data management practices to maintain data quality over time.
9. Ensuring Interoperability: Interoperability is crucial for ensuring that different systems and technologies work together effectively. Use standard data formats and protocols to facilitate seamless communication between systems. Regularly test and update integrations to maintain functionality.
Change Management
The human element is a critical factor in the successful implementation of supply chain automation. Managing change effectively ensures that your team embraces new technologies and processes.
10. Preparing Your Team for Automation: Communicate the benefits and goals of automation to your team early in the process. Involve employees in planning and decision-making to gain their buy-in and support.
11. Training and Development Programs: Provide comprehensive training programs to equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to operate new automated systems. Offer ongoing development opportunities to help them adapt to evolving technologies.
12. Managing Resistance and Fostering a Culture of Innovation: Address any resistance to change by listening to employee concerns and providing clear, consistent communication. Foster a culture of innovation by encouraging employees to experiment with new ideas and technologies. Recognize and reward efforts to embrace and drive automation initiatives.
By following these steps, businesses can effectively implement supply chain automation, ensuring that it delivers maximum benefits and supports long-term strategic goals. The process requires careful planning, technology selection, integration, and change management, but the rewards in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and competitiveness make it a worthwhile investment.
Supply Chain Automation in Practice
Supply chain automation can transform various segments of the supply chain, providing significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance. This section explores how automation can be applied across key supply chain segments including
- procurement,
- inventory management,
- order fulfillment,
- logistics,
- finance automation.
1. Procurement Automation
Procurement Automation refers to the use of digital technology to streamline and enhance the procurement process from end to end.
It encompasses automating the routine tasks and workflows associated with procuring goods and services, thereby reducing manual efforts, minimizing errors, and speeding up transactions.
To demonstrate the transformative power of procurement automation, let's consider the procurement process automated with Nanonets Procurement Automation Software:
Need Identification (Automated): Nanonets seamlessly integrates with your preferred documentation software, initiating the workflow whenever a new Needs Assessment Report is submitted in your documentation application.
Supplier Evaluation and Selection: The procurement team manually evaluates suppliers and selects the most suitable vendor. If the vendor is not already in the ERP system, a vendor account is created.
Contract Negotiation (Streamlined): Nanonets offers digital contract management, aiding in the creation, negotiation, and signing of contracts. The procurement team can use templates, track changes, and manage approvals directly on the Nanonets platform, simplifying the negotiation process.
Purchase Order Processing (Automated): The team creates digital POs on Nanonets, which are then sent directly to suppliers via email.
Delivery and Inspection: The team manually verifies the receipt of goods against the PO and contract terms, generating a Goods Received Note upon confirmation.
Invoice Capture (Automated): Invoices are captured instantly using mobile technology and seamless integrations to import receipts from your applications and databases.
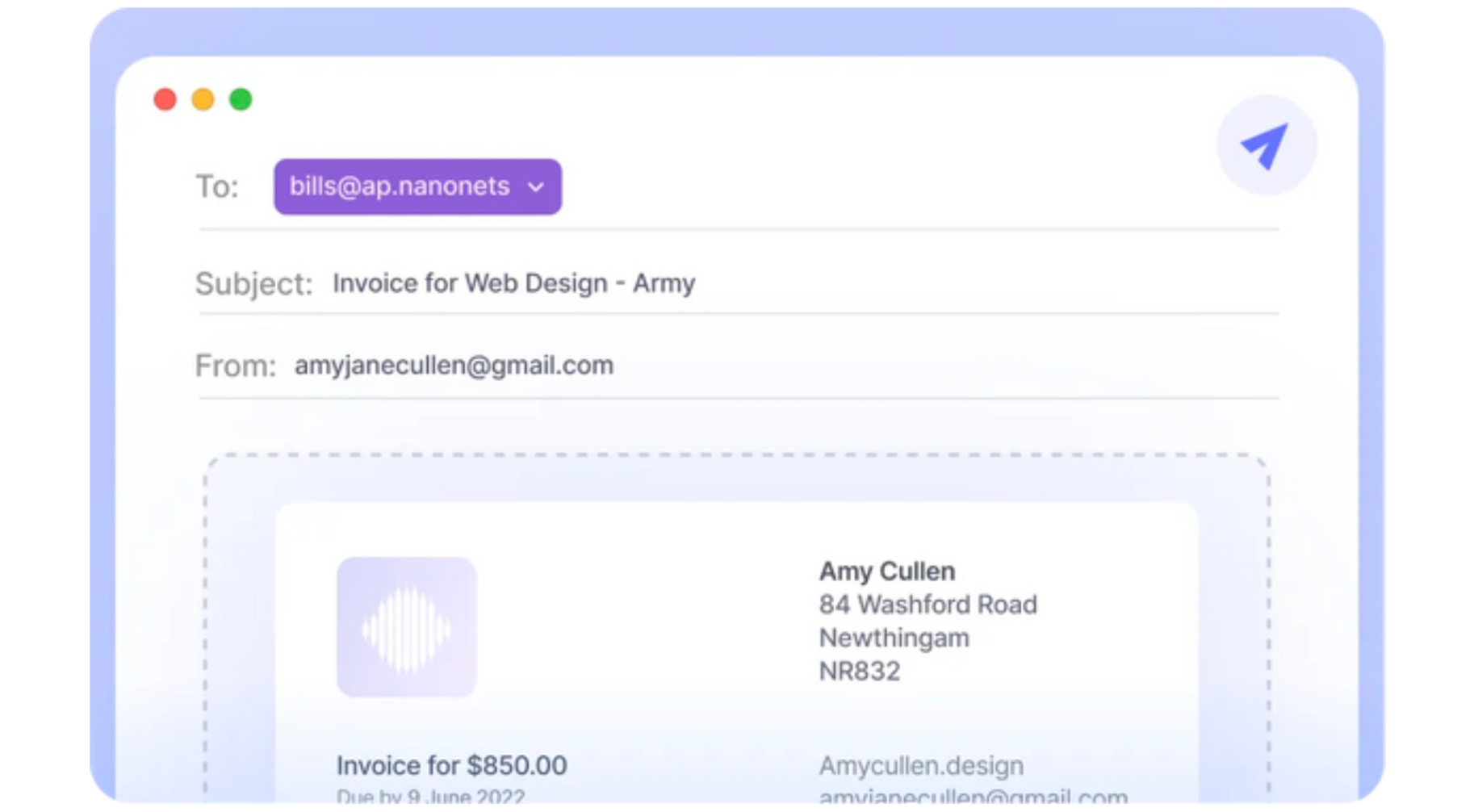
Data Extraction (Automated): OCR technology extracts structured data from invoices into digital formats rapidly.
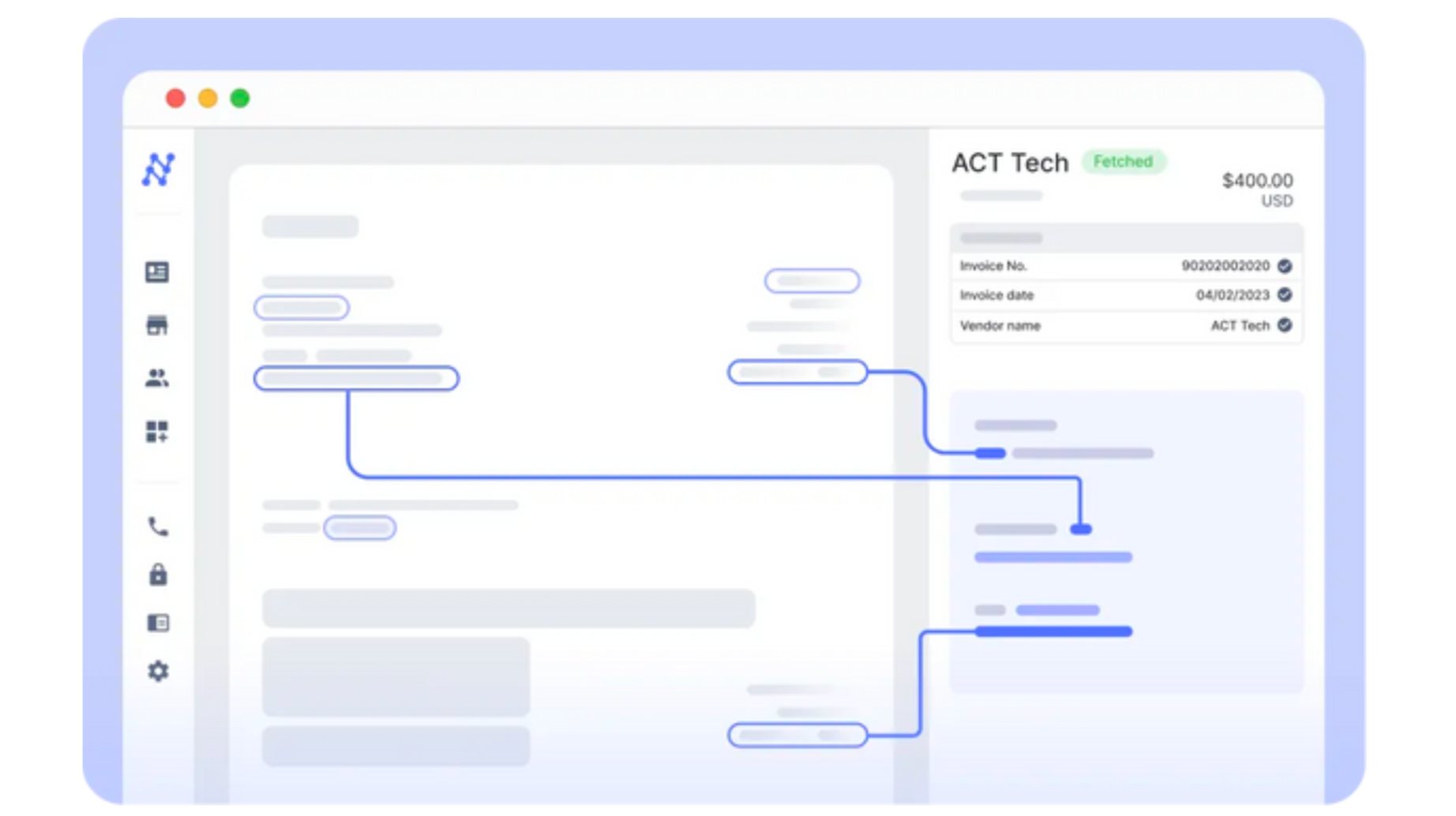
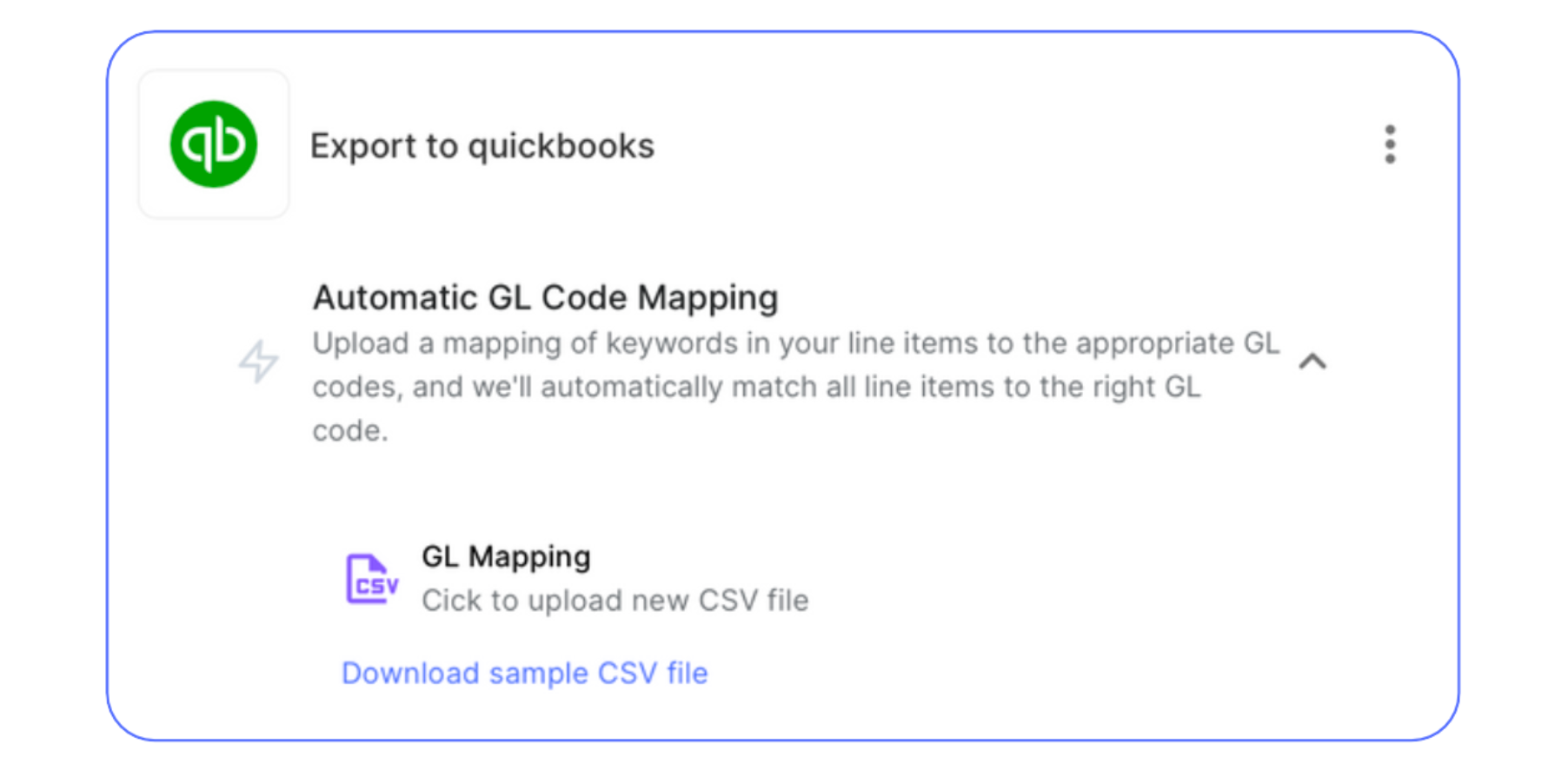
GL Coding and Data Export to ERP (Automated): Nanonets utilizes NLP and LLMs to automate GL coding, syncing data with your ERP and other applications immediately.
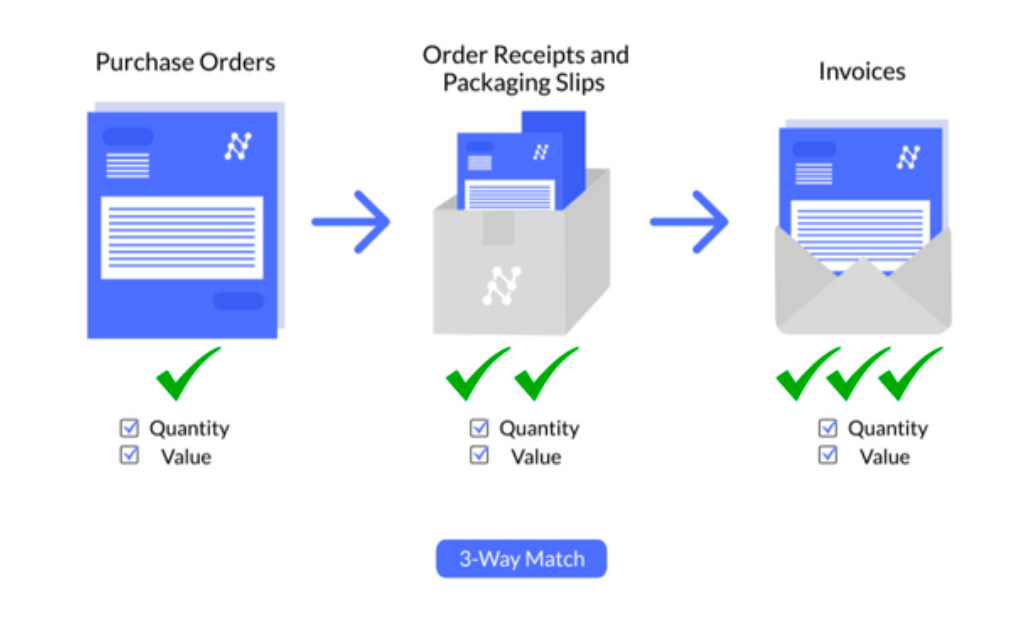
Three-Way Matching (Automated): Automated three-way matching compares POs, delivery receipts, and invoices, identifying any discrepancies.
Approvals (Streamlined): With Nanonets, approvals are flexible and integrated into your organization's communication channels, such as email, Slack, or Teams, eliminating the need for disruptive phone calls and frequent reminders.
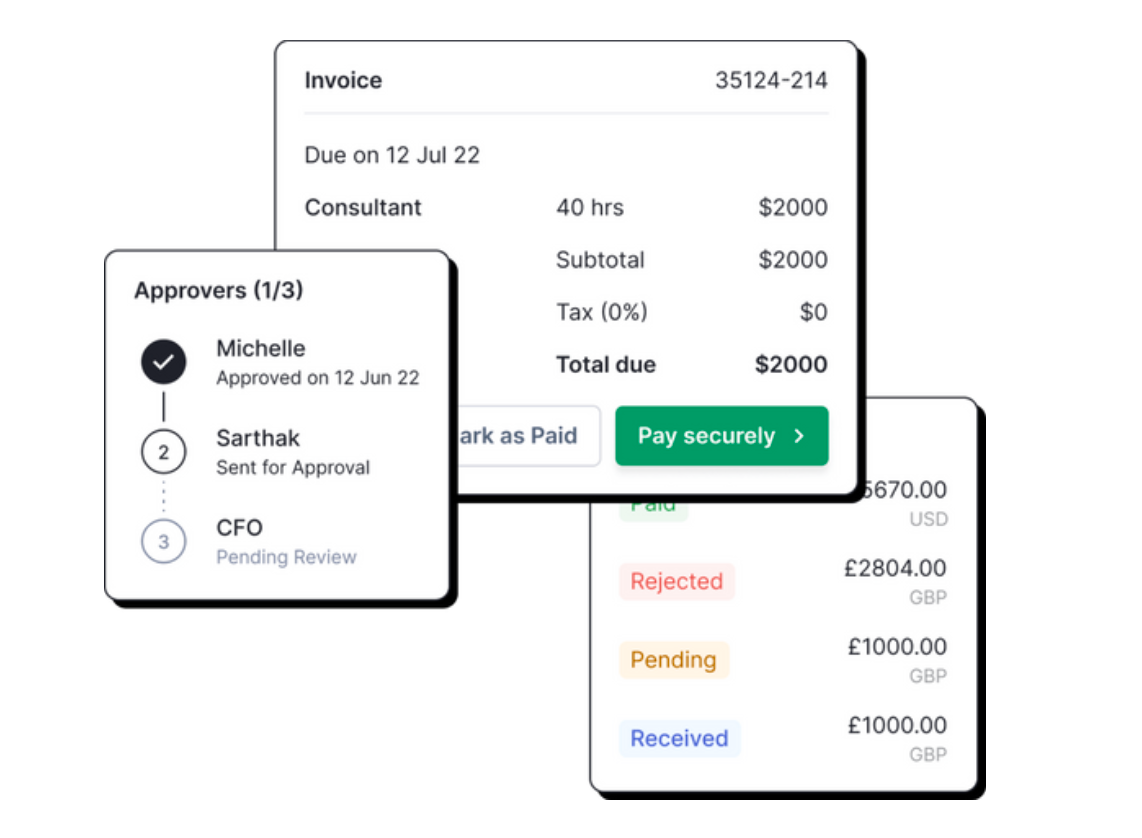
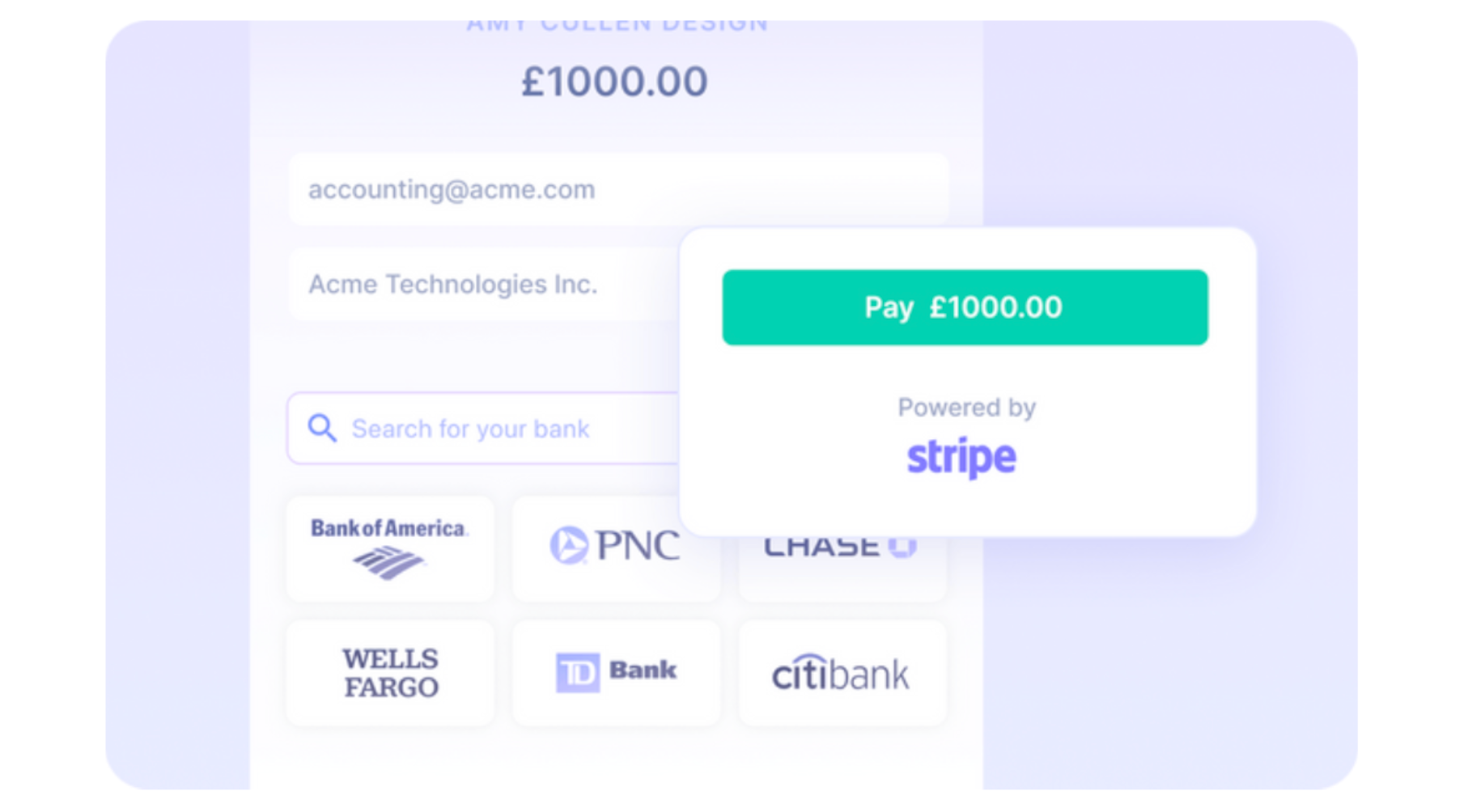
Payment Processing (Automated): Direct payments can be made globally using Nanonets, which handles forex charges and avoids unexpected chargebacks.
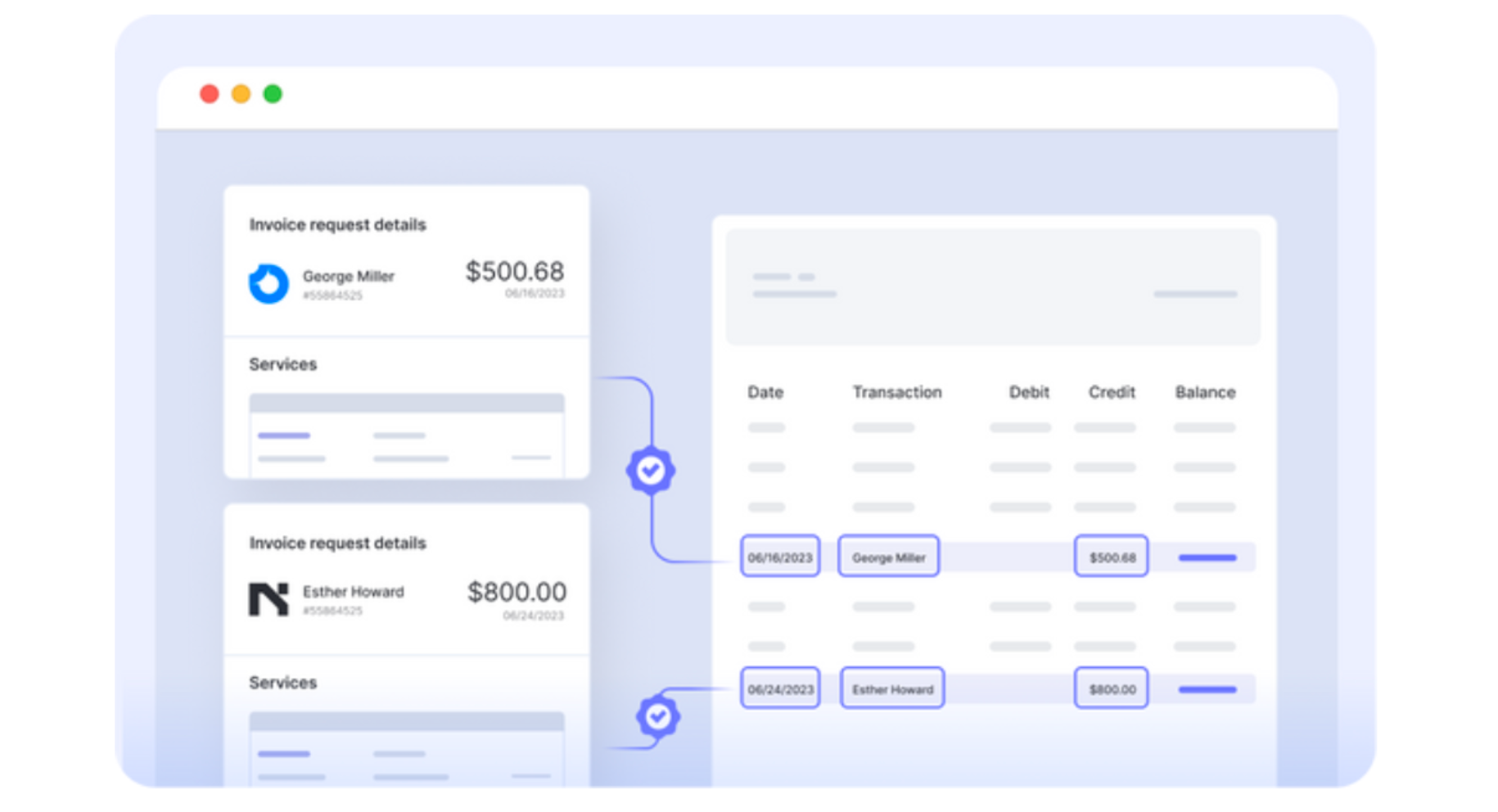
Reconciliation (Automated): Automatic reconciliation imports bank statements, matching transactions with ledger entries quickly, reducing what used to take days to just minutes.
Thus, procurement automation with Nanonets transforms the traditional procurement process into an efficient, data-driven, and strategic function. It not only reduces the burden of manual tasks but also empowers finance teams to focus on higher-value activities like cost optimization, strategic sourcing, and building supplier partnerships.
2. Inventory Management Automation
Effective inventory management is critical to maintaining optimal stock levels and ensuring product availability.
.png)
Automation technologies provide real-time visibility and control over inventory, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
Here are specific ways in which automation helps in inventory management.
- RFID and Barcoding automate the data capture process, reducing the need for manual entry and the associated errors. They provide instant updates on inventory levels as items are scanned upon receipt, movement, and dispatch.
- IoT Sensors: IoT sensors can monitor environmental conditions (e.g., temperature and humidity) in storage areas, ensuring optimal conditions for sensitive products and reducing spoilage or damage.
- Demand Forecasting: Automated systems analyze patterns in sales data, seasonality, and market trends to forecast demand accurately. This ensures that inventory levels are aligned with expected sales, reducing the risk of stockouts and excess inventory.
- Inventory Optimization: Automation tools recommend optimal reorder points and quantities, taking into account lead times, supplier performance, and safety stock levels. This helps in maintaining a balanced inventory that meets customer demand without tying up too much capital in stock.
- Order Processing: Automation ensures that orders are processed quickly and accurately, with real-time updates to inventory levels as orders are received and fulfilled.
- Picking and Packing: Automated systems optimize picking routes within the warehouse, reducing travel time and improving efficiency. They also verify that the correct items are picked and packed, minimizing errors.
- Inventory Reports: Automated systems generate real-time reports on inventory levels, turnover rates, stock aging, and other key metrics. These reports help managers make informed decisions about inventory management and purchasing.
Software Solutions for Automated Inventory Management
1. NetSuite Inventory Management
NetSuite offers a comprehensive inventory management solution that integrates with its ERP system. It provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, demand forecasting, and automated order management.
Features: Real-time inventory tracking, demand planning, automated replenishment, order management, and reporting.
2. Fishbowl Inventory
Fishbowl Inventory is a popular inventory management software that offers robust automation features for small to mid-sized businesses. It integrates with QuickBooks and other accounting software.
Features: Barcode scanning, order management, inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and reporting.
3. Order Fulfilment Automation
Order fulfillment is a critical component of the supply chain, encompassing the entire process from receiving an order to delivering it to the customer.
Automation in order fulfillment ensures efficiency, accuracy, and timely delivery.

Functions of Order Fulfillment Software
- Order Entry:
- Integrates with multiple sales channels, including Amazon, eBay, Shopify, WooCommerce, and more.
- Centralizes order management from various platforms into a single interface.
- Order Validation:
- Validates order details, including address verification and product availability.
- Flags any issues for review to ensure accurate order processing.
- Order Routing:
- Automatically assigns orders to the best fulfillment center based on inventory levels and shipping preferences.
- Supports multiple warehouses and fulfillment locations.
- Inventory Management:
- Updates inventory levels in real-time as orders are processed.
- Syncs inventory data across all connected sales channels.
- Picking and Packing:
- Generates pick lists and packing slips.
- Optimizes picking routes to improve warehouse efficiency.
- Supports barcode scanning for accurate item selection.
- Shipping Management:
- Calculates shipping rates and selects the most cost-effective shipping method.
- Prints shipping labels and customs documentation.
- Integrates with major carriers like USPS, UPS, FedEx, DHL, and more.
- Order Tracking:
- Provides real-time tracking information to customers.
- Sends automated shipping notifications and delivery updates.
- Returns Management:
- Simplifies the returns process with automated return labels and tracking.
- Updates inventory and processes refunds or exchanges.
- Customer Communication:
- Sends order confirmation, shipping, and delivery emails.
- Provides a branded tracking page for customers.
Solutions for Order Fulfilment Automation
1. ShipStation
ShipStation is a popular order fulfillment software designed to streamline and automate the entire shipping process for e-commerce businesses.
It integrates with numerous sales channels, carriers, and marketplaces, making it a versatile solution for managing orders and shipments.
2. Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a comprehensive order fulfillment service that allows businesses to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers.
Amazon handles storage, packing, shipping, and customer service for these products, leveraging its extensive logistics network.
4. Logistics Automation
Logistics automation software plays a crucial role in optimizing and streamlining logistics operations.

Here are the main functions it performs:
Transportation Management
- Route Optimization: Calculates the most efficient routes for deliveries to reduce travel time and fuel costs.
- Carrier Selection: Automates the process of selecting the best carriers based on cost, service level, and delivery time.
- Load Planning: Optimizes the loading of vehicles to maximize space utilization and minimize the number of trips.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
- Shipment Tracking: Provides real-time visibility into the location and status of shipments.
- ETA Predictions: Estimates accurate delivery times based on current traffic and weather conditions.
- Condition Monitoring: Monitors the condition of goods in transit, such as temperature and humidity, to ensure product quality.
- Customer Notifications: Sends automated notifications to customers regarding order status, shipping updates, and delivery confirmations.
Customer Service Enhancement
- Self-Service Portals: Provides customers with self-service portals to track orders, request services, and access shipping information.
- Customer Support Automation: Uses chatbots and automated systems to handle customer inquiries and support requests efficiently.
- Feedback and Satisfaction Tracking: Collects and analyzes customer feedback to improve service quality and customer satisfaction.
Logistics automation software encompasses a wide range of functionalities designed to streamline logistics operations, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. By automating key processes and providing real-time visibility and control, these systems enable businesses to achieve higher levels of performance and customer satisfaction in their logistics operations.
Explore more here - https://www.gartner.com/reviews/market/transportation-management-systems
5. Finance Automation
Finance automation is a vital component of supply chain automation, focusing on automating financial processes that are integral to the smooth functioning of the supply chain.
By integrating financial operations with supply chain activities, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and financial control.
This section explores the key aspects of finance automation within the context of supply chain automation.
Key Components of Finance Automation in Supply Chain
You may explore each use case further in detail by following the links given below
Accounts Payable (AP) Automation

- Invoice Processing: Automates the capture, validation, and approval of supplier invoices. This reduces manual data entry, accelerates payment cycles, and minimizes errors.
- Invoice Matching: Matches invoices with purchase orders and receiving documents to ensure accuracy and prevent discrepancies. This process helps in identifying and resolving issues promptly, reducing the risk of overpayments or fraud.
- Payment Processing: Streamlines the payment process by automating the scheduling and execution of payments. This ensures timely payments, which can improve supplier relationships and take advantage of early payment discounts.
Accounts Receivable (AR) Automation

- Invoice Generation: Automates the creation and distribution of invoices to customers, ensuring consistency and accuracy. This speeds up the billing process and reduces the likelihood of errors.
- Payment Tracking: Tracks payments from customers in real-time, providing visibility into outstanding invoices and helping to manage cash flow more effectively.
- Collections Management: Automates the collections process, sending reminders and follow-ups to customers with overdue payments. This improves the efficiency of collections and reduces the days sales outstanding (DSO).
Expense Management

- Expense Reporting: Automates the submission, approval, and reimbursement of employee expenses. This streamlines the process, reduces administrative burden, and ensures compliance with company policies.
- Spend Analysis: Provides detailed insights into spending patterns, helping businesses identify areas for cost savings and budget optimization.
Examples of Finance Automation Software
1. Nanonets
Nanonets is a cloud-based finance automation solution designed to automate each of the finance functions mentioned above.
2. SAP Concur
SAP Concur is a comprehensive expense management and invoice automation solution that integrates seamlessly with SAP's ERP system.
5. Warehouse Management Automation
Warehouse management automation software is designed to streamline and optimize warehouse operations by automating various tasks and processes.
Key Functions of Warehouse Management Automation Software
- Warehouse Layout and Space Utilization
- Slotting Optimization: Optimizes the placement of products within the warehouse based on factors such as demand frequency and item size.
- Space Utilization: Monitors and manages warehouse space to maximize storage capacity and efficiency.
- Labor Management
- Task Assignment: Automates the assignment of tasks to warehouse staff based on priority and availability.
- Performance Tracking: Tracks employee performance and productivity, providing insights for workforce optimization.
- Receiving and Putaway
- Automated Receiving: Scans and records incoming shipments, updating inventory levels automatically.
- Putaway Optimization: Determines the most efficient locations for storing incoming inventory, reducing handling time and effort.
- Security and Compliance
- Access Control: Manages user access to sensitive data and systems, ensuring security and compliance with industry standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that warehouse operations adhere to relevant regulations and standards, such as FDA guidelines for perishable goods.
Examples of Warehouse Management Automation Software
- Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management: Manhattan Associates provides a robust warehouse management system (WMS) designed to optimize warehouse operations through advanced automation technologies.
- Softeon Warehouse Management System: Softeon WMS is a flexible and scalable warehouse management solution that automates and optimizes warehouse processes for enhanced performance.
Supply chain automation in practice, through solutions like Nanonets, significantly enhances efficiency, accuracy, and strategic decision-making across all key segments, from procurement to logistics.
By automating routine tasks and providing real-time insights, businesses can focus on higher-value activities, driving overall performance and competitive advantage.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
To ensure that supply chain automation initiatives deliver the desired outcomes, it is crucial to measure success and continuously seek improvement.
This involves identifying and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and leveraging data to optimize processes.
Let's quickly discuss the essential metrics for supply chain performance, how to track and analyze these metrics, and strategies for continuous improvement.
Key Metrics and KPIs for Supply Chain Performance
- Order Accuracy Rate: Measures the percentage of orders delivered correctly without errors. High order accuracy indicates efficient order processing and fulfillment.
- On-Time Delivery Rate: Tracks the percentage of orders delivered on or before the promised delivery date. This metric is crucial for assessing the reliability and efficiency of logistics and transportation.
- Inventory Turnover: Calculates how often inventory is sold and replaced over a period. A higher turnover rate indicates efficient inventory management and demand planning.
- Cycle Time: Measures the total time taken to complete a process, such as order fulfillment or procurement. Shorter cycle times reflect more efficient operations.
- Perfect Order Rate: Combines several metrics (on-time delivery, order accuracy, and complete orders) to provide a comprehensive view of order fulfillment performance.
- Cost per Order: Tracks the total cost associated with processing and fulfilling an order, including labor, materials, and transportation. Lower costs per order indicate more efficient operations.
- Return Rate: Measures the percentage of orders returned by customers. A lower return rate typically indicates higher product quality and order accuracy.
- Warehouse Utilization: Assesses the percentage of warehouse space used effectively. Higher utilization rates suggest efficient use of storage capacity.
How to Track and Analyze These Metrics
- Data Collection: Utilize automated systems to collect data in real-time from various points within the supply chain. This includes ERP systems, warehouse management systems, and transportation management systems.
- Dashboard and Reporting Tools: Implement dashboards and reporting tools that consolidate and visualize key metrics, providing a clear overview of performance. These tools enable managers to quickly identify trends and areas needing attention.
- Benchmarking: Compare performance metrics against industry standards or historical data to identify strengths and areas for improvement. Benchmarking helps set realistic targets and measure progress over time.
- Root Cause Analysis: When performance metrics indicate problems, conduct root cause analysis to identify underlying issues. This involves analyzing data and processes to pinpoint the source of inefficiencies or errors.
Further Scope of Improvement
Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining and enhancing the effectiveness of supply chain automation. Leveraging data, incorporating feedback, and staying current with technological advancements are key to ongoing optimization.
- Predictive Analytics: Use predictive analytics to anticipate future trends and demand patterns. This enables proactive adjustments to inventory levels, production schedules, and logistics plans.
- Process Optimization: Regularly analyze process data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Implement changes to streamline workflows, reduce cycle times, and improve resource utilization.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor key metrics and KPIs to track performance. Use this data to make informed decisions and implement corrective actions promptly.
- Technology Scanning: Stay informed about the latest technological advancements in supply chain automation. Regularly assess new technologies for potential implementation.
- Scalable Solutions: Implement scalable solutions that can grow with your business. This ensures that your supply chain remains adaptable to changes in demand and market conditions.
Remember, measuring success and striving for continuous improvement are critical components of effective supply chain management.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Automation
The future of supply chain automation is poised to be transformative, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain technology.
- AI will enhance predictive analytics, enabling more accurate demand forecasting and inventory management. Machine learning algorithms will optimize logistics by predicting potential disruptions and suggesting proactive measures.
- IoT devices will continue to provide better real-time visibility into the supply chain, allowing for more efficient tracking of goods and assets. This connectivity will lead to smarter warehouses, where automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and drones can streamline operations, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
- Blockchain technology promises to revolutionize supply chain transparency and security. By providing a decentralized ledger of transactions, blockchain ensures traceability and authenticity of goods, reducing fraud and enhancing trust among stakeholders.
- Additionally, the integration of robotic process automation (RPA) with continue, and paired with AI will further streamline administrative tasks, such as order processing and invoicing, freeing up human resources for more strategic roles.
- Sustainability will also drive future trends, with automated systems optimizing resource use and reducing waste. Companies are increasingly adopting circular economy principles, where automation helps in recycling and reusing materials efficiently.
These advancements will collectively create more resilient, transparent, and efficient supply chains, ready to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving global market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, supply chain automation is not just a technological advancement but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to remain competitive in today's fast-paced market.
By leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, OCR, RPA, and IoT, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Solutions like Nanonets enable businesses to automate and optimize every aspect of their supply chain, from procurement and inventory management to order fulfillment and logistics.