What Is Contract Intelligence?: Definitions, Benefits, & Platforms
Download the expert's guide to Contract Intelligence now!
Samuel Goldwin famously said, “A verbal contract is not worth the paper it’s written on”. While paper contracts continue to be used now, with the digital transformation of all workspaces, they may not be worth the paper either, and digital contracts may soon become the only form of contract recognized and shared by the business place. Going even a step further, contracts could not only be stored and shared digitally but also managed by intelligent machines, thereby leading to a culture of contract intelligence.
What is contract intelligence? Where does it fall in the realm of contract management? What are its benefits and drawbacks?
Definitions: Contract, contract management, contract analysis, and Contract Intelligence
Contract
A contract is an agreement between two or more participants of activity – be it entrepreneurial, social, or personal – who come together and collaborate towards specific end goals that benefit all of them. They could be partnership contracts, employment contracts, and takeover/bid/merger contracts, among numerous others in the business sector, licensing-based contracts in the public sector, and marriage and other personal contracts. Contracts are legal obligations and are enforceable by law.
Contracts have been part of the business domain since times immemorial, with the earliest record of the law of contract dating back to 6th century Rome.
Contract management
A contract is simply a collection of words on a paper unless its terms are understood, analysed and implemented. The creation of a contract, its analysis and execution, in effect, contract management, is often crucial for both the operational and financial performance of an enterprise.
Contract management is an umbrella term that covers the creation, analysis, implementation, and all other aspects of a contract. Contract management is not an easy task. This is especially true for large enterprises that work with multiple stakeholders and have a range of competencies. Contract management in such cases can be challenged by
- Large volumes of contracts and addendums, that are not easy to track manually
- An absence of a centralized repository of contracts and access to all stakeholders
- The specialized contract language, terms, and clauses could make them unintelligible to all stakeholders
Even small companies with fewer contracts require efficient contract management because its absence can cause between 5% and 40% of the value on a given deal according to Harvard Business Review. Such losses can result from unwanted termination of contracts, legal action against breach, missing important deadlines and dates, regulatory fines, and ambiguity in roles and responsibilities in the contract.
Contract Analysis
A significant aspect of contract management is contract analysis – a thorough and critical evaluation of the contract to enable its effective execution. Review and analysis of contracts involve verification of the terms and conditions of the contract, fulfilling regulatory requirements, flagging changes brought on by new legislation, assessing corporate risk across the complete set of contracts, and verifying the wording of the contract so that there are no loopholes or ambiguity during the implementation of the contract clauses.
Contract analysis was conventionally performed manually and is ridden with pitfalls that are discussed in the next section.
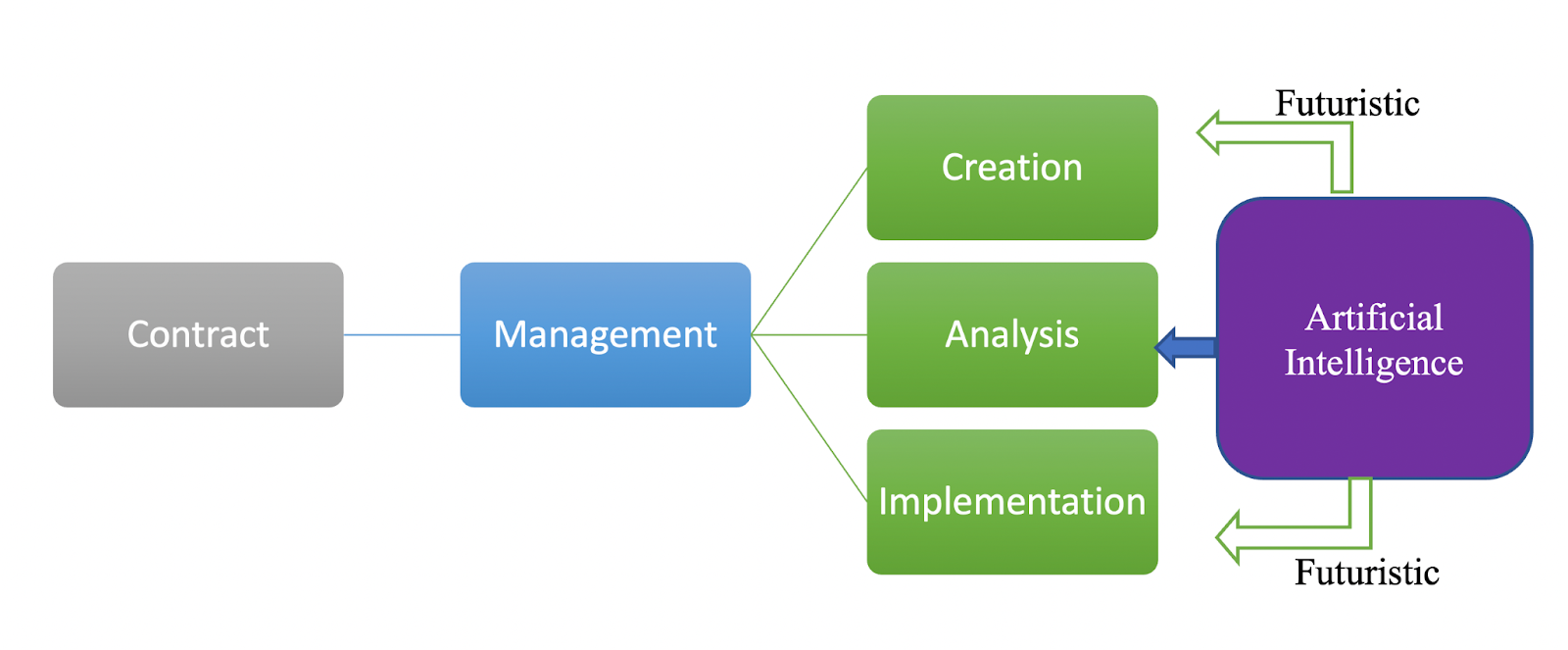
Contract Intelligence.
Contract Intelligence is the use of AI tools in contract analysis. The power of AI tools are used to extract valuable business assets from static contracts and can protect all stakeholders from legal issues and contract breach risks, and enhance productivity.
In effect, Contract Intelligence, is the use of AI tools to perform the critical task of contract analysis, to avoid the pitfalls associated with manual contract analysis.
Pitfalls of manual contract analysis
The examination and understanding of the key terms and provisions of contracts is critical to prevent the known pitfalls of contract management. Manual contract analysis faces many insurmountable challenges.
- Delays: Manual contract review is a time- and effort-intensive process. A legal team, either as part of the enterprise, or from outside is often needed to analyse contracts before implementation. Contracts are usually many pages long, and are associated with multiple sections, iterations, amendments, clauses and other legal elements. Careful analysis of all of these elements can take even the most competent legal professional days or even weeks. Additionally, contracts are not one-size-fits-all type; so each contract must be verified meticulously, which leads to excessive time delays. The Association Of Corporate Counsel (ACC) reported in 2018 that in-house legal departments reviewed an average of 173 contracts per legal employee.
- Cost: A legal team costs money. Analysis of contracts costs money. World Commerce and Contracting estimates that the average cost of a simple contract is $6.900, with costs significantly accelerating with the size and scope of the contract.
- Human errors: Manual Contract analyses are prone to oversight and human errors. Since a contract usually involves many stakeholders and participants, there is a high risk of miscommunication and errors thereof. The failure of a contract analyser to catch these mistakes opens the enterprise and all participants to risks of legal repercussions, loss of revenue and damaged relationships, both at personal and company levels.
- Structural complexity: A contract is usually characterized by jargon and unstructured or variably structured formats. It may comprise several sections, sub-sections, paragraphs, logos, and an aggregate of different types of clauses, elements, complex tables and more. The devil, as it is said, is in the details of the contract. It can get overwhelming for a human analyser to look at all of these elements critically, especially when constrained by deadlines.
- Version complexities: A contract is seldom a sign-here-now-and-we-are-on-track activity. Even during creation, there are bound to be variations and versions, and even after the contract is signed, there could be amendments and adjustments. Contract analysis requires meticulous tracking of the versions, changes, and amendments, which could be a nightmare when done manually.
- Tracking contract risks: Contract Analysis must identify the risks within the contract. It is imperative to promptly identify and act on the risks to avoid financial loss and non-compliance, and this can be difficult when performed manually.
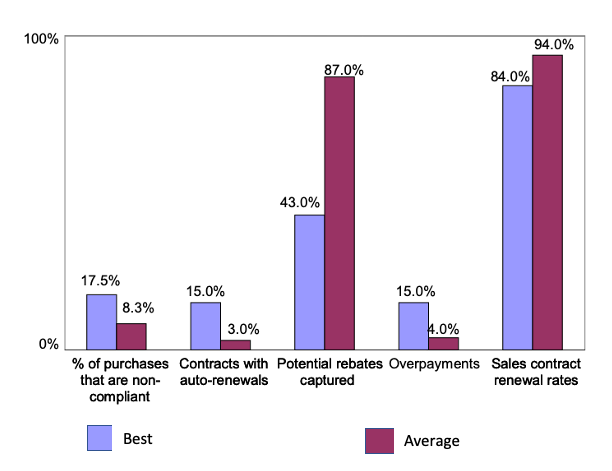
Intelligent Contract Analysis
Specialized software tools have been used for contract analysis for a couple of decades now, but these standard contract analysis systems serve merely to extract simple terms and clauses like names of the parties or termination dates. The advent of Artificial Intelligence in the past decade has enabled automation of all forms of analytical activities including contract analysis. Contract intelligence uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities to extract, understand and interpret the meaning of provisions in a contract.
Contract Intelligence tools allow easy and accurate extraction of all relevant data from a contract portfolio in a manner amenable to performance insights and risk analytics, thus removing many of the drawbacks mentioned in the earlier section of manual contract analysis.
Practical applications of Contract Intelligence
Contract Intelligence, although largely seen in the area of contract analysis, can ideally be used across the entire contract management protocol:
- Data Extraction & Classification: The use of Natural language Processing (NLP) and ML-based data extraction from contracts can encompass data pre-processing, automated data extraction, and raising of exceptions, all of which are repetitive mundane jobs when done manually. Intelligent clause detection can enable other contract management entities to easily access pertinent information such as contract clauses within their organization’s pre-approved clause library easily. Contract intelligence tools can be configured to meet the contract management needs of the enterprise.
- Contract Creation: With all the data extraction and classification possible with AI-enabled contract management, contract creation can be made simple too. ML tools learn as they are used, and they can use the information extracted from earlier contracts, and create a framework of new contracts that can be further fine tuned by a human in the loop.
- Information security: Contract intelligence can enable organizations define rules of access for various levels of data and information culled from contracts. Given the proprietary and often secretive nature of contracts and fine prints, such information security is critical in contract management.
- Streamlining Contract Workflow: High-end contract intelligence tools allow automation of the contract workflow with periodic checks and reroutes for approvals, exception handling and automated communication among all the stakeholders. Such automated workflow analytics and notifications can help in early detection of bottlenecks and anomalies within their workflow process, which can, in turn reduce the contract lifecycle and enhance contract management efficiencies.
- Smart risk management: AI tools can be used to provide intuitive graphics with the contract data to provide risk mapping and rating facilties. AI platforms can create risk assessment matrices that can analyse risk probability patterns and risk exposure. Knowledge of risks can help in planning course corrections and contract modifications. Risk management is a major factor for contract accountability and AI tools can offer a range of innovative functionalites for better source-to-contract risk assessement.
ML and Neural Network techniques can enable understanding of keywords specific to contracts. For example, they can help recognize
- Jargon-driven description of dates (“not later than fifteen business days after demand therefore”) and amounts (“equal to five percent (5%) of the shareholders’ equity of AB, Inc,”)
- special contract-specific phrases that mean the same thing, like “upon execution of this agreement” and “when the contract is signed”. Both phrases mean the same and are recognized as such by contract intelligence tools.
- semantic similarity (even if the wording is different)
- provisions and clauses correctly, even in cases of varied formulation
Benefits of Contract Intelligence
According to Gartner, by 2024, the amount of manual effort for the contract review process will be reduced by 50% of what it is today due to adoption of AI-based contract analytics solutions. This is driven by the following benefits of Contract Intelligence
- Transparency: Automated Contract Analysis enables transparency across the enterprise’s contract portfolio not only through digitizing the information and associated artifacts and storing them in a central repository, but also enable analytics through tools such as neural networking and machine learning. Thus, smart extraction of obligations, service levels, and other key information like milestones, deliverables, and KPIs can ensure intended business outcomes are delivered.
- Risk mitigation: The ML tools in contract intelligence allows timely identification of errors, incorrect contract language, and other drafting errors so that remedial actions may be embarked on without delay.
- Optimization of the contract creation process: AI tools can be used to mine information from an existing portfolio of contracts as well as past performance data, thereby providing pointers to relevant clauses, terms, and positions that work with the competence of the enterprise. Such insights help in drafting future contracts with better risk management.
- Better contingency response: A classic example of unexpected happenings disrupting contracts is the recent COVID pandemic, during when, businesses had to analyse and redesign their legacy portfolio to identify places in the contracts that would be affected by the pandemic and associated lockdowns. The use of AI tools in the entire contracting process can help in dealing with such unexpected events and can help in reorienting contracts to meet the force majeure of nature.
- Better business decisions: Good business decisions are built on sound data. The contract repository can be used as a source of business intelligence that can help make strategic decisions both during contract framing and during implementation. This functionality is especially useful during renewal of contracts, wherein smart analytics of contract vis-à-vis performance data can help in deciding the clauses in future contracts.
Contract intelligence in compliance review
The use of AI in contract management can simplify regulatory compliance:
- Ensuring regulatory compliance requires sifting through pages of clauses, sections, obligations, regulations etc., a task that can take legal and compliance teams, days. The use of AI based automation can help digitize the contract documents, pick out keywords, track omissions, and provide insights about the steps to follow.
- Regulations and compliance rules are often updated and modified. Matching all contracts with the updated and modified compliance rules can be a management nightmare. AI tools can help collate all contracts in one location, and then help in automatic sifting through the contracts to find areas of mismatch with the updated regulations, thereby ensuring full compliance at all times.
- AI tools in contract intelligence can also take over the communication aspect of contract management so that all stakeholders are kept aware of regulations and compliance facts and of any mismatch between contracts and the regulatory requirements. This empowers all stakeholders of the contract and affords audit trails across the regulatory landscape.
- Technologies like advanced analytics, machine learning, and deep learning can identify any discrepancies in contract compliance and performance obligations and flag alerts immediately so that rectification steps may be carried out in time to avoid regulatory pitfalls.
Limitations of a contract intelligence platforms
As with any technology-enhanced process, contract intelligence is not without limitations, many of which can be overcome by judicious choice of the platform of implementation.
- The first deterrent to the use of AI tools in any process is that it is expensive and time consuming to implement. Any new technology is associated with such issues at first, but with greater use, these impediments can be overcome to some extent. As for the expense, the enterprise is required to perform a cost-benefit analysis to see if the contract intelligence platform would indeed, in the long term, have favorable RoI.
- The implementation of any new technology is associated with a learning curve. Contract intelligence offers complex functionalities, which is both a benefit and a detriment – benefit because of the obvious performance enhancement, but deterrent because implementation and use requires a certain amount of specialized skill set that must be developed. The incorporation of contract intelligence in an enterprise must necessarily including a training element, in which the stakeholders are trained to various levels of expertise as per their involvement in the contract.
- A common sentiment among many people is that while it is human to err, it takes a machine to foul things up. This need not necessarily be true and arises from a fear of the unknown. Attitude orientation and employee training can help in enhancing trust on technology among the stakeholders in the contract.
- The functionalities of the AI-enabled contract management must be commensurate with the management needs of the enterprise. A company that only deals with employment contracts needs a simpler contract intelligence platform, compared to a multinational company that deals with mergers, acquisitions, sales and stocks, in addition to employee onboarding.
How to choose a contract intelligence platform?
The basic factors that govern the choice of a contract intelligence solution are
- The level of automation required: The levels of functionalities required of the enterprise’s contract management practices must be taken into account while choosing a contract intelligence platform. In addition to the company's needs, the choice of the platform also depends on its ability to commit to that level of technology, and fit with the work culture.
- Budgetary constraints: As mentioned earlier, contract intelligence entails the procurement of technology and expertise. This hinges on the amount of money available, which is dependent on the scale of the business, the bottom line, and the company's investment potential.
- Ease of use: The implementation of contract intelligence requires a certain amount of human involvement and therefore requires a specific skill set. The need for training and tech support must be addressed before choosing the right tool.
- The number of stakeholders involved and the organizational hierarchy: Contract intelligence enables better visibility to all stakeholders, at varying levels depending upon the stakeholder participation levels in the contract. Contracts may involve approvals and signatures, and the contract intelligence tool may be chosen to perform tasks like workflow management, approval routing, etc.
- Integration with the other systems used in the company: While contract intelligence can be a standalone entity, it can also be integrated into a larger hyper-automation system of an organization. The need and usefulness of hyper-automation in the present or a future period must be assessed before choosing the contract intelligence tool. In the event of future integration, the tool must be compatible with the larger system of business process automation.
- Repository setup: Contract intelligence engines digitize the entire portfolio of legacy contracts. The enterprise can decide where the digitized data is to be stored and choose a platform that fits with this requirement.
- Deep data extraction: Contract Intelligence can go beyond simple data extraction and allow categorization and analysis of data that provide insights into clauses, obligations, service levels, rate tables, and more. This is a functionality that most contract management workflows would need, and the choice of a platform must check for availability of these features
Answers to a few FAQ on Contract Intelligence
Can the AI engine read the contract thereby compromising confidentiality and data safety?
This question arises from the general mistrust on machines. AI tools are algorithms that make predictions and analysis based on data patterns. Thus, although machine learning learns what to do, it can’t discern it the way humans do. So, unless there is an evil Bond villain extracting the data from the ML and commanding it to do evil tasks, there is no risk of AI engines (or ATMs as Sheldon fears) leading the charge of the machine brigade.
Can Contract Intelligence extract data in a meaningful way?
Meaningful to humans, yes. Based on rules and learning from experience, the engine can pick out data and information and classify them in a way that is meaningful to the human-in-the-loop. As answered in the previous question, machines don’t find meaning in data the way humans do. At least yet.
Is the information provided by Contract Intelligence reliable?
The ML learning accuracy is fairly high to start off, and improves with use. In any case, AI based contract management can be as efficient or more efficient than manual management, with the added advantages of time savings and reorientation of human effort into more meaningful activities.
Take away
Contract intelligence is a new approach to contract management that enables dynamic analysis of contracts in the context of the competence of the enterprise. AI tools used in contract intelligence ensure the realization of the intent of the contract throughout its lifecycle, while also providing real-time, high-impact insights that help with compliance and successful contract management. Contract intelligence can minimize risk and trigger appropriate actions with changes in regulations and business environment. It can learn and grow with the enterprise, thereby serving an organic extension to an otherwise inorganic assist tool.


