
Invoices—they’re everywhere. If you're here, that means you are looking for an easier way to keep track of them without losing your mind (or your invoices!)
That’s where invoice readers come in. These tools aren’t just fancy add-ons for your accounts payable team.
Imagine an OCR tool that digitizes your invoices, automates data entry process, and seamlessly integrates everything into your accounts payable system. No more manual sorting, no more errors, and a lot more time to focus on what actually matters.
Let’s dive into why invoice readers are becoming a must-have:
The evolution of invoice readers
While almost 70% of global invoice processing remains paper-based, more companies are recognizing the benefits of digital invoice processing.
A McKinsey report reveals that higher-growth companies generate nearly 90% of their invoices digitally – 10 percentage points more than their lower-growth peers.
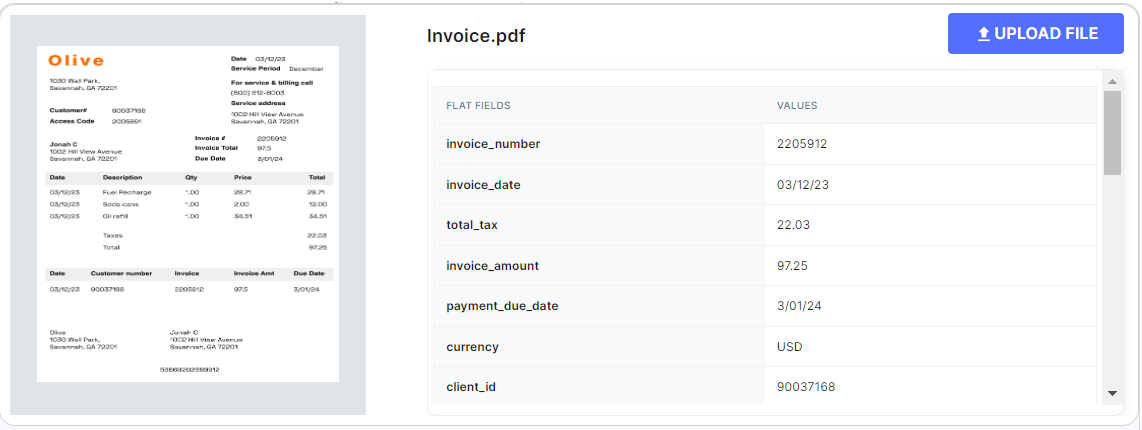
This shift from manual ledgers to digital formats like PDF invoices is transforming financial processes, offering increased efficiency and accuracy.
Some of the formats of digital invoices are:
- Visual Digital Format Invoices: JPG, PNG, GIF (picture formats), TIF (from scanning software) and PDF: These are simply digital images of the paper invoice.
- Data Digital Format Invoices:
- Unstructured - The data cannot be automatically read from the document into accounting systems. These are free form texts such as contracts, letters, articles, and memos that may double as invoices in some unstructured, small businesses.
- Structured – The data is in structured form and may be as Spreadsheets (e.g., Excel), tables in word processors such as Word (.doc), HTML XML Data PDF EDI (EDIFACT) and CSV.
The evolution of invoice reading has been rapid in recent years:
The first generation of invoice reading: Manual
Each invoice, in whatever digital form it is, is manually read, and relevant data is extracted and stored in a uniform system that bypasses the format variations of the various invoices received. This is old-fashioned, involves intensive human labor, and is time-consuming, error-prone, and unsuitable for large companies that deal with many invoices on a daily basis.

The second-generation: Invoice reader software
Also known as the invoice recognition software, the data from digital invoices, irrespective of their original format, are captured by software based on recognition of key data fields. The data thus read is stored in easy-to-access applications such as a spreadsheet or a database. OCR technology is used for this purpose. While better than manual data entry, OCR could be restrictive in that developers must set up rules and templates to capture data, and a certain amount of manual intervention is needed to check for accuracy.
The third-generation: AI-based invoice readers
Artificial intelligence-based invoice readers, often available as invoice reader online platforms, can intelligently capture relevant data with minimal errors due to the continuous learning processes of the AI. It allows the reading software to adjust to all formats of invoices and gives it a universality across the company’s platforms. Also, these invoice readers easily adapt to various invoice formats, eliminating the need for manual template creation.
What are AI-powered OCR invoice readers?
Software used to automatically read invoices can work on either second-generation or third-generation technology. Since each invoice holds key data used in accounting resource planning and decision-making within the business, accuracy in data extraction is essential.
The data thus read from invoices are usually then transferred to ERP, accounting, or data analytics platforms used by the company for subsequent processing.
An effective AI-powered AP invoice reader must have the following features:
- The capability of accurately extracting data that may be structured, poorly structured and/or unstructured in the original invoice. The coherence of data extracted from these various sources is eased through the use of AI-based [data extraction].
- The ability to process multiple invoice types and formats from different sources.
- The capability of converting the extracted data into multiple readable/editable formats for subsequent use.
- Data security - since invoices involve financial data, they can be highly sensitive and the software used for automated invoice capture must be able to ensure safeguarding financial data from theft, hacking, and mismanagement.
How AI-based invoice reader OCRs work
- Document ingestion: The reader automatically imports various invoices from various sources including email, cloud storage, or online forms.
- OCR data extraction: The OCR engine converts the invoice image into machine-readable format, recognizing characters, numbers, symbols, and other details.
- AI-powered data interpretation: Machine learning algorithms understand the invoice's context and structure, identifying key fields and line items without predefined templates.
- Data validation: The platform cross-references extracted data for consistency, flags potential errors, routes exceptions for human review, and applies business rules to ensure accuracy.
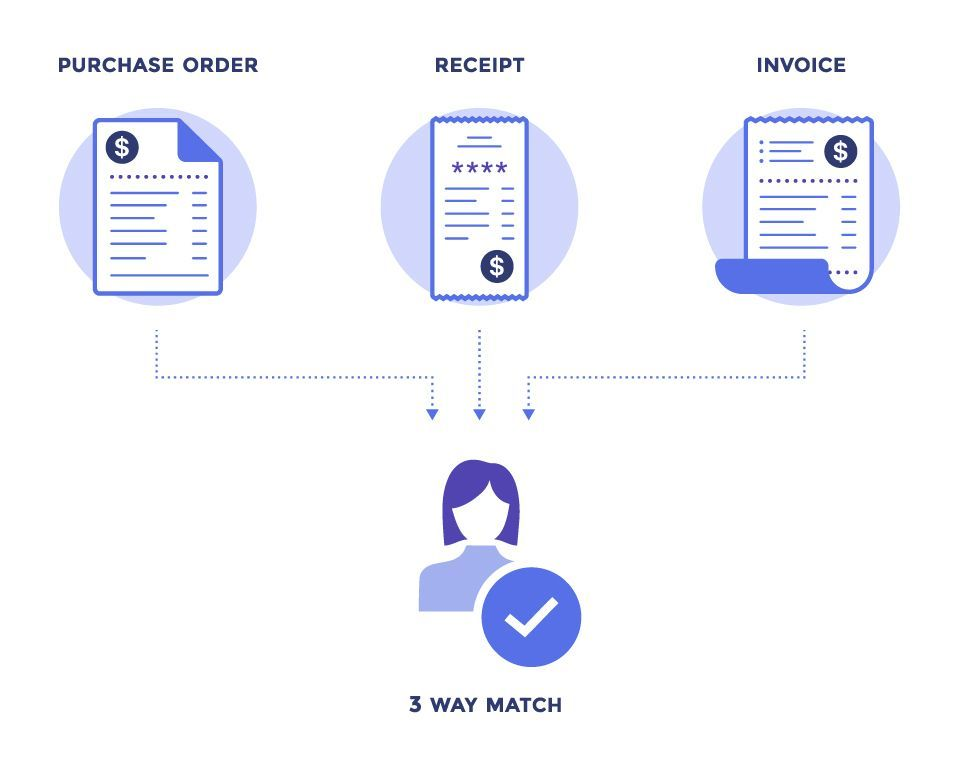
- Purchase Order matching: The system automatically matches the invoice with corresponding purchase orders, comparing line items, quantities, and prices to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Integration: Validated data is automatically populated into accounting or ERP systems in real time, streamlining the accounts payable workflow.
The AI-OCR platform improves its accuracy over time by learning from each processed invoice. This continuous learning process enables the system to adapt to new invoice formats and variations, reducing the need for manual intervention. Moreover, automating the accounts payable workflow allows your AP team to focus on more strategic financial tasks.
Advantages of the invoice reader software
- Accuracy of data: Accurate invoice data extraction helps prevent duplicate payments and overpayments.
- Time savings: Manual invoice reading is time-consuming, and automation can save much of the time spent by employees in mundane repetitive activities.
- Employee reorientation: The time available to the employee due to automation of invoice reading can be rerouted to productive tasks that can enhance their skillset and the company’s bottom line.
- Centralization of data: The data captured by the invoice reader online can be stored in a centralized location, often in the cloud, and therefore will be accessible to all stakeholders of the company from anywhere with internet access.
- Detect fraud: Invoice readers can automatically flag discrepancies between purchase orders and invoices before payment is made.
- Security of data: The possibility of introducing checks at various levels of the automation process initiated by the invoice reader can enhance data security.
- Scalability: As the business expands, it is cumbersome to have a manual system for [invoice management]. An automated invoice reader can streamline the process, leading to scale-up enhancements.
- Better vendor relations: Faster invoice processing can lead to more timely payments and improved vendor relationships.
- Save money: Streamlined invoice processing often results in capturing more early payment discounts and prompt payments.
Modes of automated invoice reading
The reading of relevant fields in invoices of various formats is not trivial. Despite the progress made by AI and machine learning in recent years, the identification of complex patterns in invoices is challenging, but modern invoice readers have been steadily improving in this regard.
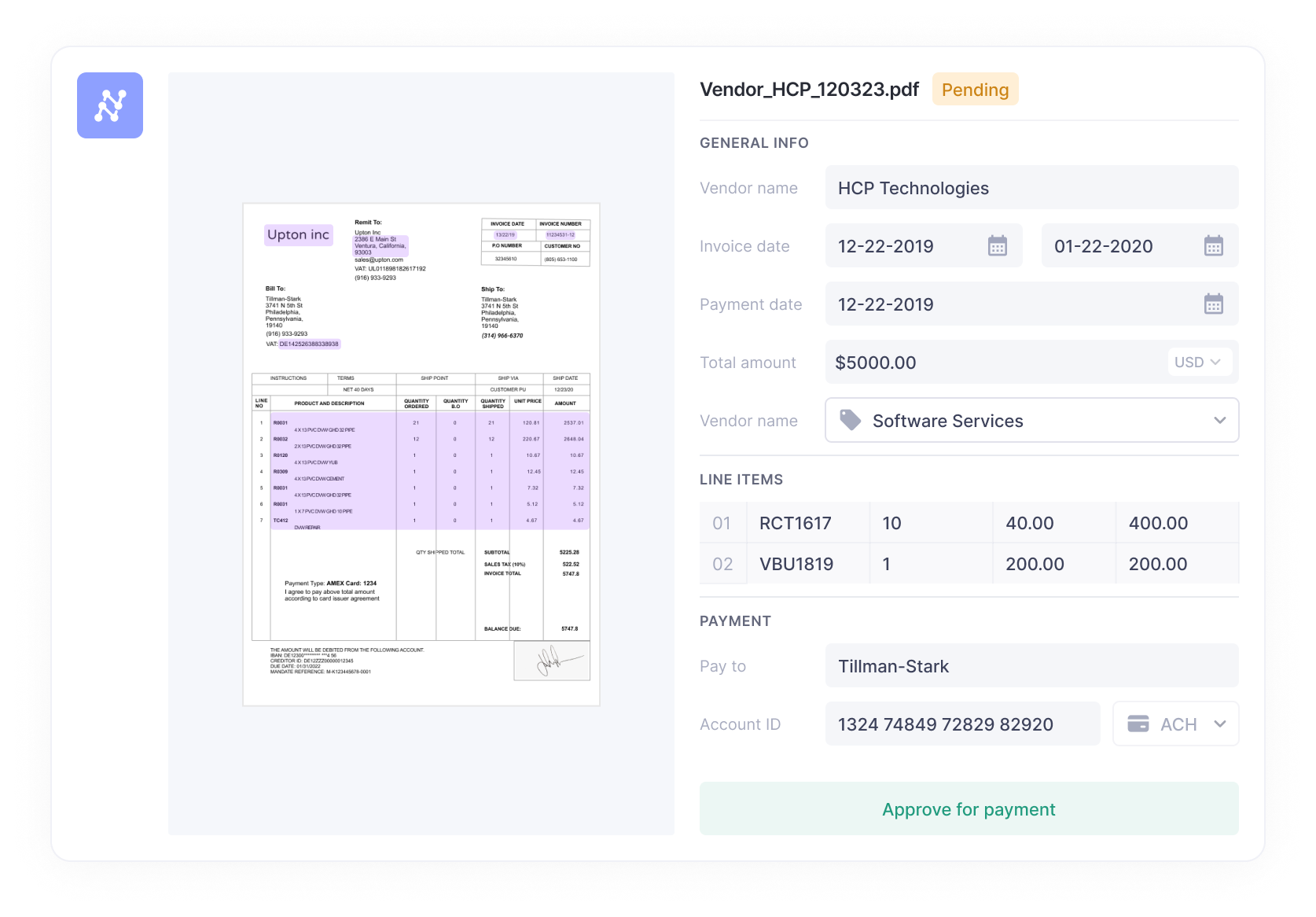
With known formats of invoices, e.g. from long-term clients who have not changed their invoice formats drastically, zonal OCR and keyword-based pattern matching can enhance accuracy and reliability in invoice reading.
Zonal OCR for invoice readers
The zonal OCR software can be trained to identify the structure and hierarchy of a known invoice through code or API. PDF invoice readers typically fall under this category. The OCR engine splits the document into physical “zones” that could correspond to a particular field. These zones are determined through the design of appropriate OCR templates.
They are usually location-based, as shown in the following figure, in which, the user simply draws a square around data that must be extracted. Then, rather than reading the page as a single entity, the data in the specified zones are extracted as specified in the template.
OpenCV, Tesseract, and Python are some zonal OCR systems that can be trained to pick out specific fields from a scanned document. The invoice2data python package, for example, reads data from defined fields in invoices. It extracts structured data from PDFs using a template system. Other OCR libraries can also be used for python invoice readers.
Python invoice readers and PDF invoice readers can also extract line-items from invoices, which can be useful because the product information can be stored along with the classic invoice data such as date, number, and amount. This is especially useful to obtain fine-grained data that must be fed into a subsequent ERP system.
Pattern-matching and keyword searching invoice readers
Instead of or in addition to zonal OCR based invoice reading, intelligent filters can be used to isolate specific data that may be present in varying locations in invoices. These keyword filters work by checking for specific data forms (like numbers or currency symbols) in the entire document and searching for keywords around it to categorize the numbers into types like date, quantity, amount, etc.
For example, when there is a dollar sign (“$”) in a pdf invoice, the reader can be trained to search for the words “Amount due” or “total due” or “total” immediately next to the sign and pick up the numbers that follow the dollar sign, to save under an appropriate handle such as “Total amount due”.
Keyword-based extraction is suited to read the metadata files such as total, date and number, and is not particularly suited for line items in invoices.
Challenges to automated invoice reading
Invoice reader software could fail when fine-grained table data are to be extracted from an invoice, the layout of which is unknown at that time. Zonal OCRs could fail in extracting data from semi-structured documents, in which the fields to be extracted are not in the same position in all the documents.
The extraction of text from complex data fields, such as multi-line postal addresses is also challenging. Another difficulty that many invoice readers face is in the extraction of sequential data fields (e.g. continuing product numbers in the same invoice or receipt).
A solution to the above problems is to adopt a hybrid model in which an additional layer of human data validation is included in the invoice capture step. While the computer can do a large fraction of the job of invoice capture, the manual intervention can be kept minimal, only to validate the extracted data, thereby not adding to human labour time and effort significantly.
Another solution to the invoice reading challenges is Electronic Data Interchange or EDI. In EDI, instead of companies exchanging invoices in a format recognizable to humans alone, transactional data are exchanged between companies in a machine-readable format. The machines, in effect, “talk to each other”. This can obviate manual intervention. This however is not a universal solution yet because a majority of businesses worldwide still deal with invoices either in paper formats, or other human-readable digital formats like PDF.
Artificial Intelligence-based readers can also circumvent many of the above problems. Nanonets is an OCR tool that leverages AI & ML capabilities to automatically extract unstructured/structured data from PDF documents, images, and scanned files. Unlike traditional OCR tools, Nanonets doesn’t require separate rules and templates for each new document type.
Things to remember when adopting an invoice reader software
To select the best invoice-reading software for your business, consider the following factors:
- The infrastructure and IT resources required to support the invoice reader
- The financial commitment involved in setting up and running the system
- The ability to integrate with other systems within the company
- The levels of automation and human intervention required/possible within the business
- Availability of know-how within the company and customer support from the maker of the software
- The levels of data security required
- The level of access – this would decide where the data would be stored – in a local machine, a central server or the cloud
As accounts payable departments continue to evolve, adopting AI-powered invoice reading solutions becomes increasingly crucial. To start your journey towards automated invoice management system, assess your current workflow and pain points, then consider the above factors to determine the most suitable invoice reader software for your organization.
Conclusion
Embracing invoice reader software isn't just about keeping up—it's about riding the wave of financial efficiency. By automating mundane tasks, you're not only saving time but also unlocking your team's potential to focus on what truly matters: customer care, innovation, and growth. An efficient AP invoice reader does more than just process documents; it's a game-changer for your entire financial ecosystem, reducing errors, accelerating payment cycles, and providing invaluable insights into your spending patterns.
As the business world continues to evolve, staying competitive means embracing tools that streamline your operations. Invoice reader software isn't just a nice-to-have—it's becoming a must-have for modern companies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an AI-powered invoice reader?
A software that uses artificial intelligence and OCR technology to automatically extract, process, and validate data from various types of invoices, streamlining accounts payable workflows.
How does an AI invoice reader differ from traditional OCR
Unlike traditional OCR, AI invoice readers can understand context, adapt to different invoice layouts without templates, and improve accuracy over time through machine learning.
How does a PDF invoice reader work?
The platform will use OCR technology to scan PDF invoices, extract relevant data, and convert it into structured, machine-readable information for further processing.
What is OCR invoice scanning?
It is a process that uses Optical Character Recognition technology to convert printed or handwritten text on invoices into machine-readable data. This technology allows for quick and accurate extraction of important information from invoices, such as invoice numbers, dates, amounts, and vendor details, without manual data entry.
