Are you looking for an RPA solution for the government sector? Create your first automation in <15 minutes today. Used by 30k+ people from 500+ enterprises around the world. Start your free trial or schedule a call with us.
Science fiction and public sentiment have speculated on both utopian and dystopian governments are driven by automation tools and public responses have varied from dread to cautious optimism. While the private industry is already making incredible advances in incorporating automation tools into their operational structure and reaping benefits, the government sector has been slower in its adoption. Nevertheless, 21st-century digital tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA) are rapidly finding inroads into governments and governance.
This article explores various aspects of the use of RPA in government organizations and their benefits and challenges.
What is RPA in Government?
Gartner defines Robotic Process Automation, thus.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a productivity tool that allows a user to configure one or more scripts (which some vendors refer to as “bots”) to activate specific keystrokes in an automated fashion. The result is that the bots can be used to mimic or emulate selected tasks (transaction steps) within an overall business or IT process. These may include manipulating data, passing data to and from different applications, triggering responses, or executing transactions. RPA uses a combination of user interface interaction and descriptor technologies. The scripts can overlay on one or more software application.
In simple words, RPA is the use of rule-driven software tools to automate routine, repetitive, and predictable tasks through orchestrated activities that emulate human action. It eliminates human involvement in time-consuming tasks such as swivel chair data entry.
In effect, RPA improves the speed and efficiency of activities, lowers costs through automation of repetitive and mundane tasks, and allows humans to engage in more strategic tasks, all of which are good reasons for RPAs to be used in Government organizations.
Like all large businesses, governments also deal with labor-intensive, repetitive chores such as document processing, information dissemination, data management, and security compliance, which are their building blocks. Governments are recognizing the benefits offered by RPA in its functioning and are increasingly adopting various RPA tools for their activities.
Start your RPA Pilot test for free with Nanonets. No credit card is required. Forever Free plans are available. Start your free trial or schedule a call with us.
How is RPA Used in Government?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA) find diverse applications in the public sector. A common use case involves enhancing citizen services by automating repetitive, manual tasks like data entry and verification. This reduces clerical errors and response times, improving overall efficiency in government processes.
The workings of Government RPA
Any data-driven work process in the governance sector follows the sequence of actions.
data-collection =>data-classification => data-transfer
The data is finally transferred to an archive or to another sequence of events that involves processing and analytics. Given that the primary sequence is well-defined and repetitive, RPA software or bots can perform such tasks in accordance with rules set by the user.
In effect, RPA bots are designed to replicate human interactions and use Graphics User Interface (GUI) elements, and tools such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR), computer vision, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and screen scraping. In recent years, RPA is also integrated with AI tools such as Machine Learning (ML) to extend the power of process automation.
There are three types of RPA Bots that can be used in the Government sector – task bots, medabots, and IQ bots – depending on their levels of expertise.
- Task bots that are often used in the front end of applications are used to replicate rule-based tasks and can process structured data. Early versions of OCR and ICR fall under this category.
- Medabots are independent, reusable logic blocks that can be used for common user interface operations, such as logging on to a system.
- IQ bots have cognitive capabilities to process semi and unstructured data, detect patterns, and have learning features.
Automate repetitive manual tasks with Nanonets. Extract data from government documents, invoices, identity cards, or any document on autopilot! Trusted by 30k+ users. Rated 4.9 on G2.
Areas of RPA use in the public sector
Government and public sector organizations can leverage RPA for the following activities:
- Data digitization:
The conversion of physical data into digital data can help governments provide services that meet the evolving expectations of citizens. According to McKinsey & Company, government digitization, using current technology could generate over $1 trillion annually worldwide.
RPA tools from basic OCR to AI-driven RPA tools be used in government organizations for data extraction from reports, letters, memos, claims, court records, etc., and the data can be stored in a meaningful way for further analysis or archiving. Such data can be used for subsequent generations of reports on budgets, citizen services, law-and-order matters, R&D, defense matters, and so on.
- Data migration:
RPA can be used to transfer data among legacy systems and organization platforms. Bots can check for duplicates, inform users, and delete data that are deemed unnecessary. RPA Bots can retain the quality and accuracy of data without the need for human intervention.
Workload automation (WLA) – the management of workloads across physical, virtual, and cloud environments – can help governments run crucial administrative processes across from a centralized locus, thereby enhancing data-driven processes and eliminating errors.
- Communication with the public
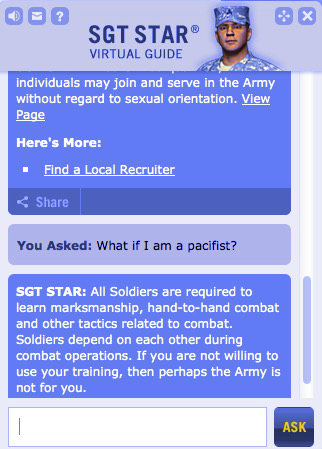
RPA-enhanced communication channels can help in information dissemination to citizens, peer-to-peer sharing of data, and co-creation of solutions with the private sector and citizens. A classic example of the use of RPA to disseminate information has been SGT STAR, an interactive virtual assistant of the US Army, that uses IQ Bot to answer questions, check users’ qualifications, and refer them to human recruiters.
The RPA tool uses machine learning to recognize data patterns that help it distinguish helpful answers from unhelpful ones. The Army found that SGT STAR does the work of 55 recruiters, with an accuracy rate of more than 94%. As of 2016, the virtual assistant had answered more than 16 million user questions.
- Public opinion analysis
RPA tools can be used to extract data from online platforms, review sites, social media sites, and maps to understand the opinions and views of the general population about government services, their needs, complaints, and feedback. Web crawling bots can pull data from online resources and further AI-based tools can analyse the data to provide an understanding of public sentiments on various matters of governance.
The US DoD’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has created the Deep Exploration and Filtering of Text (DEFT) program, which uses natural language processing (NLP) to automatically extract relevant information and help analysts derive actionable insights from it.
- Processing of applications and forms
Various kinds of forms and applications are filled by citizens via government online portals to access many kinds of services. RPA bots can mine important data from these forms and applications and validate the application, verify personal information, and approve and route them to different agencies for further action. The processing of driver licenses, passport applications, tax forms, employment records, and healthcare data can be eased by RPA tools.
For example, the Defense Logistics Agency of the US provides logistical support to the military and uses RPA to respond to bid abstracts, and for the onboarding process. EMMA chatbot developed for U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services of the Department of Home Land Security attends to requests pertaining to immigration services, green cards, passports, and other services offered by this department.
- Healthcare management
RPA can be integrated into the public healthcare sector for management. It can be used to manage public records of healthcare and vaccination information, especially during times of epidemics and pandemics, communicate with citizens about healthcare updates, and generate timely reports for Government action during health crises.
For example, the Caerphilly County Borough Council in the U.K. used RPA solutions to deal with the surge in applications for free school meals during the COVID-19 crisis. The Indian Government generated citizen passes with RPA during the Pandemic lockdowns.
- Public security:
RPA can enable safe storage of citizen data such as their National IDs, license numbers, tax IDs, and other sensitive information behind layers of security.
Use Nanonets RPA solution for Government. Automate document processes with automated workflows. Integrate Nanonets intelligent automation platform with your existing stack.
Benefits of using RPA in the Government sector
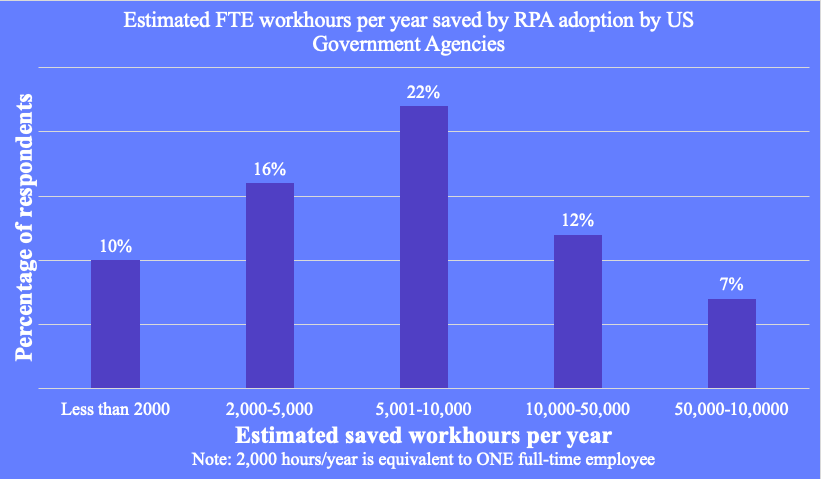
The primary driver for the use of RPA in the government sector is savings in work hours possible through the automation of mundane, time-consuming tasks. A U.S. State of Federal RPA Report from November 2020 says “the annualized hours saved by automation deployed increased from 285,651 to 848,336, a 195% increase.”
An updated report in December 2021 showed the reduction of over 1.4 million hours (and counting) of low-value work across the [U.S.] government to date.
Another survey by FedScoop and StateScoop conducted among federal and state government employees and government contractors in the US showed that workhour savings are expected to be the most compelling benefit of RPA adoption by the agencies.
Other obvious benefits of RPA adoption include
- Fiscal savings: Enhancement of operational efficiency can lead to considerable cost savings for the Government. According to Deloitte LLP, a mid-tier Fortune 1000 organization with $20 billion in revenue and 50,000 employees, can save $30 million every year with automating just 20% of its tasks through RPA. Given that any Government is much larger than a midsize company, both in terms of the number of employees and revenue, the money savings possible is mind-boggling. Within five to seven years, U.S. government agencies could save as much as $41.1 billion in annual costs, according to Deloitte. Nanonets can slah your costs by 80%. Save more with Nanonets. Try Nanonets for free.
- Enhanced operational efficiency: A survey by Governing magazine reported that 53% of state and local officials are burdened with too much paperwork that affects their efficiency. It is said that a human being is likely to make 10 errors in every 100 steps when performing redundant work. RPA does not fail from fatigue like the human brain. When coupled with cognitive analytics, RPAs can also overcome problems and bottlenecks, which can further ease the job for the human employee. Nanonets can process all your documents with >95% accuracy. Improve your efficiency now with Nanonets. Try Nanonets for free.
- Better service delivery: Citizens of all countries expect a higher level of service from government organizations in terms of faster delivery, reduction of paperwork and red tape, and better transparency of operation. RPA can help Government workers deliver reliable, open, and responsive citizen services, thereby enhancing public trust in the Government sector.
- Better decision-making: The bricks that make a society are built with the clay of data. While the amount of data available to any Government is huge, its judicious use in decision-making is hampered by the very quantum that is unwieldy for human handling. RPA enables organized data aggregation and can supply relevant and useful data both for manual decision-making and other AI tools. The use of advanced data analytics software to analyze this RPA-managed data can help both policymakers and government service executives better understand processes and workflows, and plan and process improvements to general and specific government activities.
Take data driven decisions with Nanonets. Synch all data from all documents and get the data to make better decisions. Start your free trial or schedule a call with us.
Challenges in the adoption of RPA in the government sector
A survey by Salesforce and Pulse of 100 global IT and engineering leaders showed that the biggest challenge to implementing process automation in the industrial sector was mapping complex processes and integrations, followed by other factors like implementation cost, employee resistance, building skillset, etc. as seen in the graph below
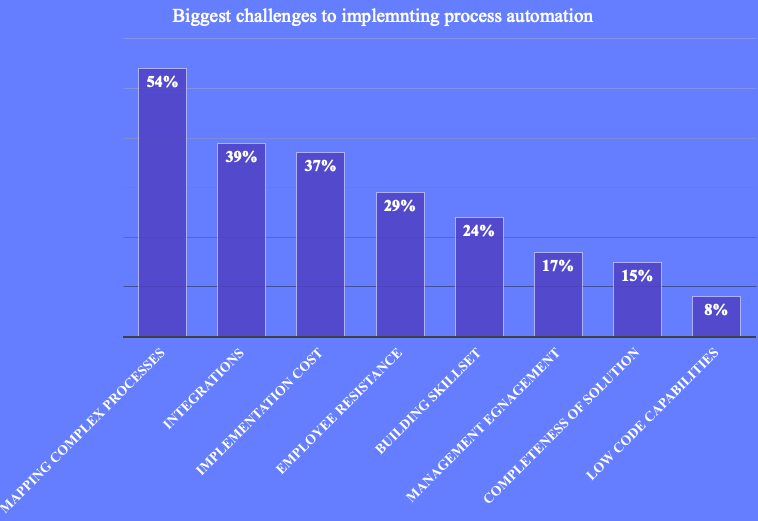
While the challenges to automation of the Government sector are the same, the relative importance varies somewhat, with employee resistance being the predominant deterrent.
- Resistance to change: Inertia is a strong force in the Government sector, in part because of its expanse of operation. The public sector is less agile to change than the private sector also due to factors such as established hierarchy, extensive red tape, and lack of incentive to change. In the private sector, change that leads to performance improvements is often fiscally rewarding to the individual, but in the public sector, there is no such incentive, which discourages employees from making changes or taking risks. An article in the Apolitical, titled “No risk, no innovation: the double-bind for the public sector” has this to say: “Government incentives for risk, meanwhile, don’t really exist. If you pull off a major improvement in service delivery, you don’t get a bump in compensation or promoted faster.”
- Lack of skill set: While RPA could be a human-independent operation, setting it up and overseeing it involves human involvement and a certain skill set. Most government personnel in non-technical roles, who will benefit from RPA, do not have enough awareness of digital data and tools. Without awareness and knowledge, it is virtually impossible to introduce a digital tool like RPA into an establishment. Even after the introduction of RPA tools into a government department, there is a need for technical staff to manage the technical and operational issues for its successful implementation. The lack of technical skillset is a major deterrent to the use of RPA in government organizations. Nanonets is easy to learn with 0 learning curve! Try Nanonets for free now.
- Poor match to the needs: Any automation tool can be useless, if not dangerous if it does not match the needs of the department or organization. Poorly matched RPA solutions can undermine worker motivation, cause alienation, and reduce satisfaction, productivity, and innovation. In the words of Bill Gates, “automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.” Thus, there is a high chance of government agencies giving up on RPA because of poor performance due to inefficient operation.
- Security concerns: Four major areas of potential security concerns regarding RPA solutions deter its more widespread use in the Government sector - Misuse of Privileged access, system vulnerabilities, system outages, and disclosure of confidential information. There are ways to mitigate these risks. Conducting regular audits and risk assessments, maintaining meticulous control over access to the RPA ecosystem, and strict system governance can help reduce or eliminate these risks and enable greater use of RPA in the public sector. Nanonets maintain the data logs for all the actions. Explore Nanonets for free now.
Want to automate repetitive manual tasks? Save Time, Effort & Money while enhancing efficiency!
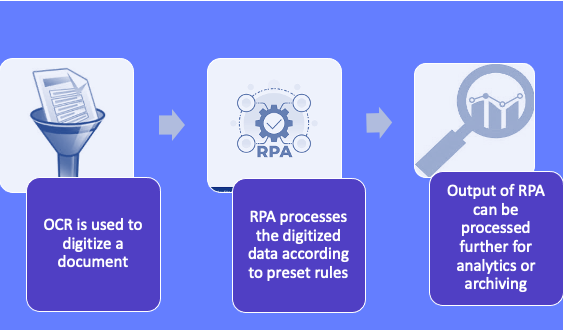
Nanonets in the RPA sequence
Nanonets is an OCR software that can be part of the RPA sequence because it leverages AI & ML capabilities to automatically extract unstructured/structured data from PDF documents, images, and scanned files. A typical sequence involving Nanonets in the RPA protocol is shown below.
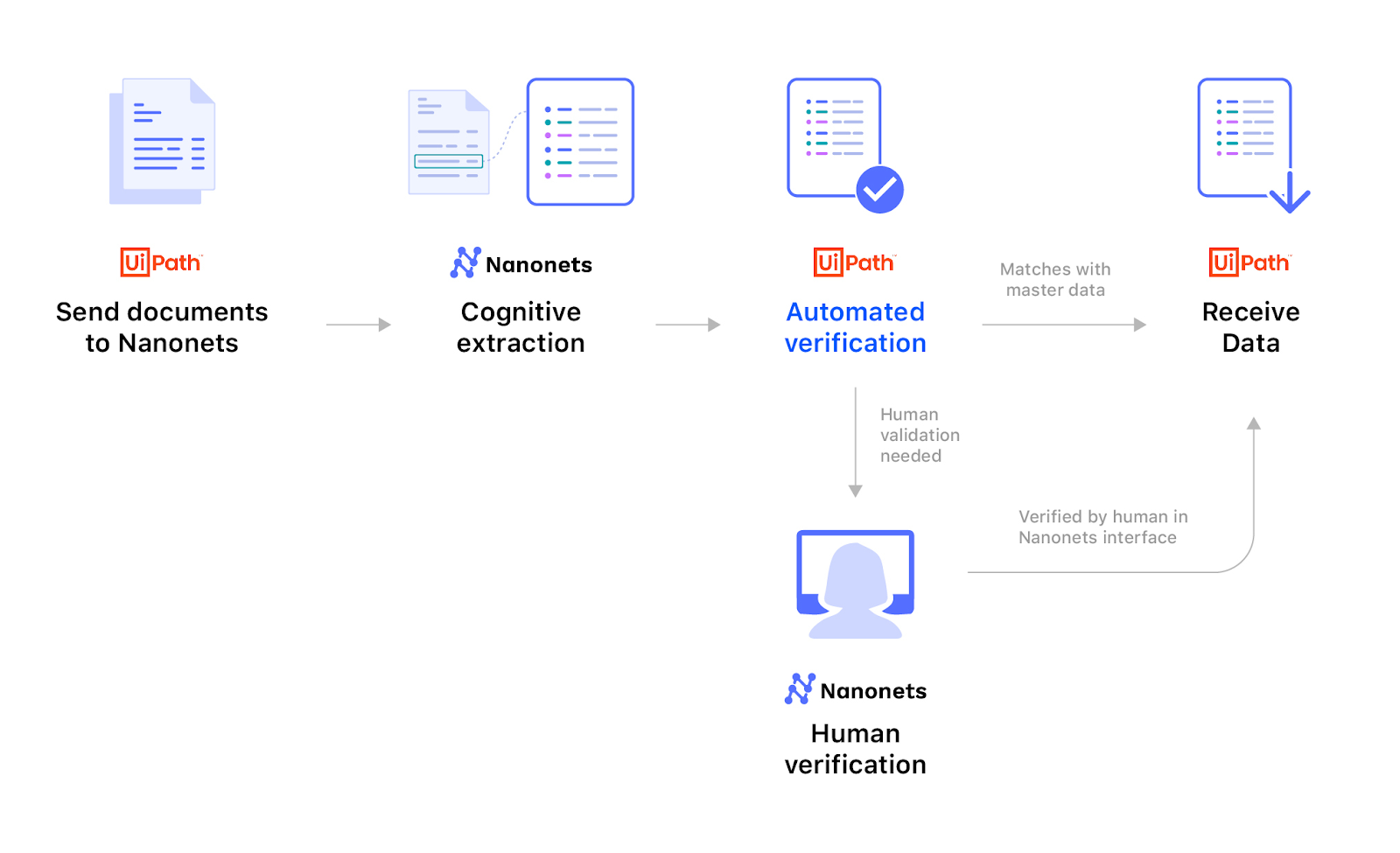
The AI-driven cognitive intelligence of Nanonets allows the handling of semi-structured and even unseen document types while improving over time, which makes it particularly useful for data-intensive public sector activities. The Nanonets algorithm & OCR models learn continuously.
The Nanonets API provides high speeds and great accuracy in line item extraction of data and drives automation for line item management. The output can be customized, to only extract specific tables or data entries of interest.
The versatility of Nanonets arises from their ability to perform the following tasks:
- Accurate detection of the table structure of a line item containing documents like forms.
- All the line item entries that are present in the forms like name, product, price, total sum, discounts, etc.
- The data can be extracted as JSON output that can enable the building of customized apps and platforms.
- While offering a great API & documentation for developers, the software is also ideal for organizations with no in-house team of developers.
This versatility allows the use of Nanonets in a variety of functions and departments within an organization – the accounts payable, HR, inventory management, etc. This makes it an ideal system to be integrated into an Enterprise Content Management setup.
Additional factors that make Nanonets a good RPA tool::
- It is a truly no-code tool
- Easy integration of Nanonets with most CRM, ERP, content services, or other RPA applications.
- No post-processing needed: Nanonets OCR can recognize handwritten text, images of text in multiple languages at once, images with low resolution, images with new or cursive fonts and varying sizes, images with shadowy text, tilted text, random unstructured text, image noise, blurred images and more.
- Works with custom data through the use of custom data for training OCR models.
- Multiple input recognition: Nanonets OCR can recognize handwritten text, images of text in multiple languages at once, images with low resolution, images with new or cursive fonts and varying sizes, images with shadowy text, tilted text, random unstructured text, image noise, blurred images, and multiple languages
- Independence from formats: Nanonets are not bound by the template of documents. You can capture data cognitively in tables or line items or any other format.
Take away
While the use of RPA and AI tools in government work has not kept pace with the rapid expansion of AI in industry, governments across the globe are slowly adopting RPA and other AI solutions for their operations. When applied strategically, RPA can help in the efficient delivery of citizen services, reducing costs and increasing citizen satisfaction and engagement with government machinery.