Let's start with a scene that’s probably familiar. It’s the end of the month, and a mountain of invoices has piled up on someone’s desk—or, more likely, in their inbox. Each one needs to be opened, read, and its data manually keyed into an accounting system. It's a slow, tedious process, prone to human error, and it’s a quiet bottleneck that costs businesses a fortune in wasted time and resources.
For years, this was just the cost of doing business. But what if invoices could just... process themselves?
That’s the promise of modern invoice data extraction. It’s not about just scanning a document; it’s about teaching a machine to read, understand, and process an invoice, so that your AP team can focus on more strategic activities. In this guide, we’ll break down how this technology works, what to look for in a real solution, and show you how we at Nanonets have been helping companies around the world process invoices faster and efficiently.
What is invoice data extraction?
At its core, invoice data extraction is the process of pulling key information like vendor names, invoice numbers, line items, and totals from an invoice and structuring it for an accounting system or ERP. It’s the critical on-ramp for automating accounts payable, and its accuracy sets the foundation for all subsequent financial record-keeping.
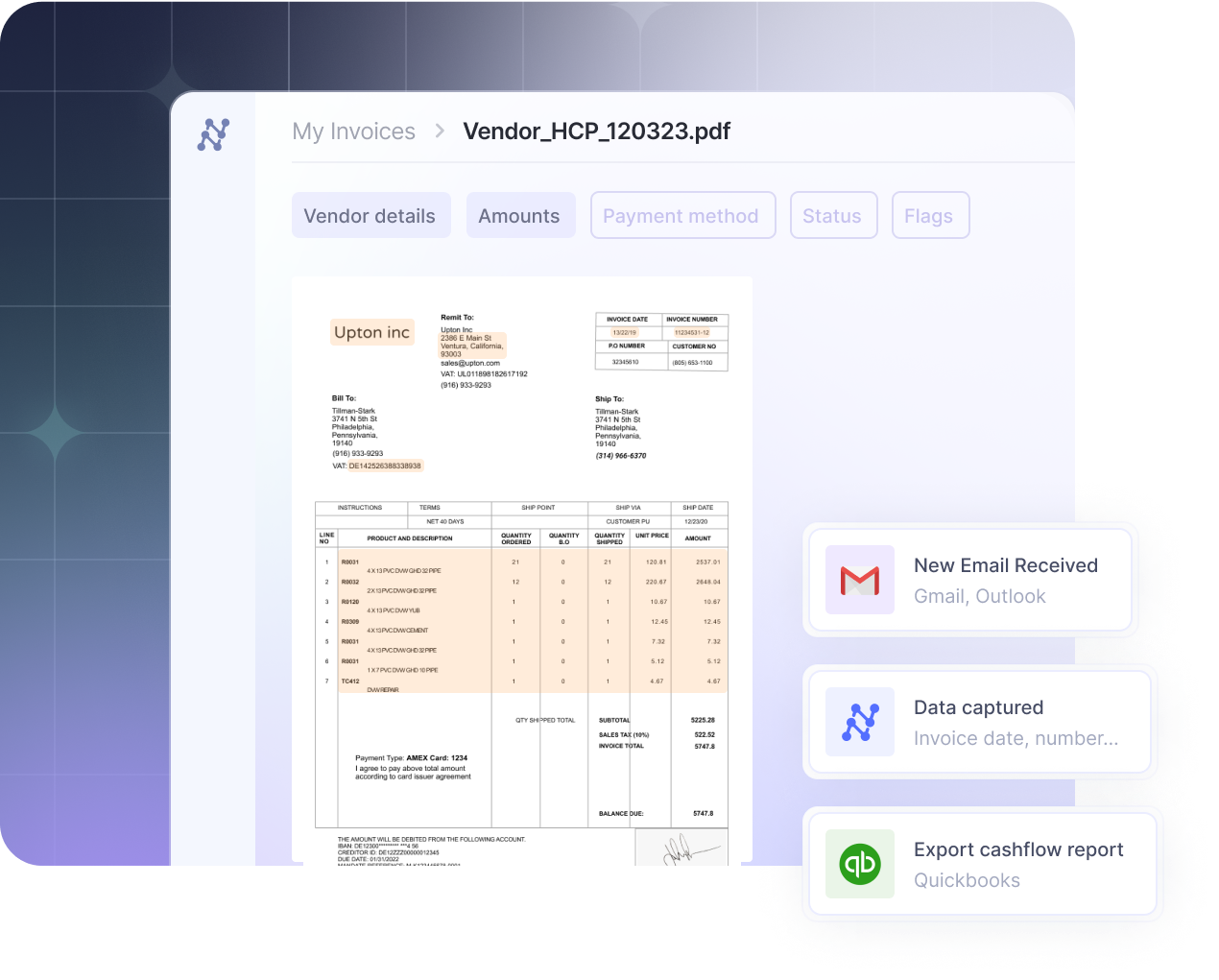
A detailed look at the invoice data you can extract
When we talk about "key information," we're referring to a wide range of data points that are crucial for accounting and operations. A modern extraction tool can capture dozens of fields, typically organized into these categories:
- Vendor information: Includes the vendor's name, address, contact details, and tax identification number (TIN).
- Invoice specifics: This covers the unique invoice number, the issue date, the payment due date, and any associated purchase order (PO) number.
- Line items: A detailed, row-by-row breakdown of each product or service, including its description, quantity, unit price, and total cost.
- Totals and financial data: The subtotal before taxes, a breakdown of tax amounts (like VAT or GST), shipping charges, and the final grand total due.
- Payment terms: Details on how to pay, including payment method, terms like "Net 30," and any available early payment discounts.
Why your current invoice process is probably costing you a fortune
The problem with manual invoice processing isn't just that it's tedious; it's that it's an incredibly inefficient use of skilled human capital like finance professionals. When a person has to handle each invoice manually, the process is slow and expensive.
Augeo, an accounting services firm and one of our clients, found that their team was spending four hours per day on manual entry. After automating, that time was cut to just 30 minutes.

The costs associated with a manual process go far beyond just the time spent on data entry:
- The hidden costs of errors: Manual data entry is prone to mistakes—studies show error rates can be as high as 4%. A single misplaced decimal or incorrect vendor ID can lead to overpayments, duplicate payments, or missed early payment discounts. The time your team spends finding and fixing these errors is a hidden operational cost that drains productivity.
- High labor costs: Your team's time is a valuable resource, and manual data entry is a significant time sink. Industry data shows that employees can spend nearly half their workday on repetitive tasks like this. Every hour spent manually keying in data is an hour not spent on strategic financial analysis, vendor management, or identifying cost-saving opportunities.
- It doesn't scale efficiently: As your business grows, the volume of invoices grows with it. With a manual process, your only solution is to add more headcount, directly increasing your payroll costs. This linear relationship between growth and overhead creates a major bottleneck and prevents your finance operations from scaling efficiently.
- Vulnerability to fraud: Manual systems lack the automated checks to easily spot suspicious activity. A fraudulent invoice, whether from an external phishing scam or an internal source, can look legitimate to a busy employee. Without automated validation against purchase orders or vendor master files, these can slip through, leading to direct financial loss.
How invoice data extraction actually works
Automating invoice extraction isn't a new idea, but the technology has evolved significantly. Getting your data from a PDF into an ERP system shouldn't feel like trying to navigate the asteroid field in The Empire Strikes Back.
The old way: the world of templates and rules
The first generation of automation relied on template-based, or Zonal OCR. Here’s how it works: for every vendor, an employee has to manually create a template, drawing fixed boxes on a sample invoice. The rule is simple: "the invoice number is always in this box, the date is always in this box."
This category includes solutions from open-source libraries like invoice2data, which uses manually created templates, to legacy enterprise platforms like ABBYY and Tungsten.
When a new invoice arrives from that same vendor, the system applies the template and extracts text from those predefined coordinates.
How it works: For every vendor, a developer creates a template by defining fixed coordinates or rules (like regular expressions) for each field on a sample invoice. The system applies this rigid template to extract data from subsequent invoices from that specific vendor.
This approach is better than manual entry, but it's incredibly brittle.
- It breaks with any change: If a vendor updates their invoice layout even slightly—moves the date, adds a logo—the template breaks, and the process fails.
- It requires massive maintenance: You need a separate, manually-created template for every single vendor. For instance, in the case of one of our customers, Suzano International, a leading Brazilian pulp and paper company with over 70 customers, it would mean creating and maintaining over 200 different automations to handle all their document formats.
- It can't handle variation: It struggles with tables that have a variable number of rows or optional fields that aren't always present.
The LLM experiment: Can a general LLM handle invoices?
With the rise of powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, a common question is: "Can't I just use that?" The answer is yes, you can upload an invoice image to a general LLM and prompt it to extract the key fields into a JSON format. It will often do a surprisingly decent job.
How it works: With a subscription to a service like ChatGPT Pro, a user can upload an invoice image and write a prompt like: "Extract the invoice_number, invoice_date, vendor_name, and total_amount from this document and provide the output in JSON format."
However, this is not a scalable business solution. Using a general-purpose LLM for a specific, high-stakes business process like accounts payable has several critical flaws:
- It's a tool, not a workflow: An LLM can extract data from a single document, but it can't automate the end-to-end process. It can't automatically ingest invoices from your email, run validation rules (like checking a PO number against your database), manage a multi-stage approval process, or export data directly to your ERP. It's a single, manual step that still requires a human to manage the entire workflow around it.
- Inconsistent output: While you can prompt an LLM to produce structured output, consistency isn't guaranteed. One time it might label a field invoice_id, the next it might be invoice_number. This lack of a fixed schema makes it unreliable for automated downstream integration, a problem users have noted when trying to build reliable solutions.
- Data privacy concerns: For most businesses, uploading sensitive financial documents containing vendor details, pricing, and bank information to a public, third-party AI model is a significant data security and compliance risk.
- It doesn't learn from your data: A specialized tool gets better and more accurate for your unique use case over time because it learns from your team's corrections. A general LLM doesn't create a fine-tuned model that is continuously improving based on your specific needs.
Using ChatGPT for invoice processing is like using a brilliant Swiss Army knife to build a house. It can cut some wood and turn some screws, but it's no substitute for a dedicated set of power tools designed for the job.
The effective way: Purpose-built AI for context-aware extraction
Intelligent Document Processing is the modern, purpose-built solution that combines advanced AI with a full suite of workflow tools.
How it works: IDP platforms are designed to be template-free. They use AI trained on millions of documents to understand the context and structure of an invoice, regardless of the layout. Here's how they work:
- Document capture and pre-processing: The process begins by receiving an invoice from any source. The system then automatically cleans the document image, using techniques like noise cleaning and skew correction to prepare it for analysis.
- Contextual analysis: This is where the real intelligence comes in. An AI model doesn't just read words; it analyzes the entire document's DNA. It looks at dozens of signals simultaneously: the exact position of a number on the page, the pattern of characters in a line, and how different text blocks are aligned. This allows it to understand context. For example, the date at the top right is the invoice_date, while a date in a table is a service_date.
- No-template learning: This rich contextual data is fed into a deep learning model that has been trained on millions of invoices. It learns the common patterns of invoices in general, which allows it to accurately extract data from a document it has never seen before without needing a pre-defined template.
- Validation and integration: After extraction, the data is automatically validated. The verified data is then seamlessly integrated into your accounting or ERP system.
This is often enhanced with Zero-Shot Extraction, a cutting-edge capability where you can instruct the AI to find a new field with a simple text description, without needing to train it on labeled examples.
What to look for in a modern invoice extraction tool
When evaluating a solution, look past the buzzwords and focus on these four core capabilities. A truly effective platform is much more than just an OCR engine; it’s a complete operational tool.
1. True AI, not just old-school OCR
The most critical feature is the ability to handle any invoice format without needing custom templates. This is the core promise of AI. A template-less system dramatically reduces setup time and eliminates the maintenance nightmare of updating templates every time a vendor changes their invoice design.
2. A complete, customizable workflow
Data extraction is only one piece of the puzzle. A real solution automates the entire accounts payable workflow. This means it must include robust features for each stage:
- Import: Flexible options to get documents into the system, such as via email, cloud storage, or API.
- Data actions: Tools to clean, format, and enrich the data after extraction.
- Approvals: The ability to build multi-stage approval processes based on your specific business rules.
- Export: Seamless integration to send the final, approved data to your accounting or ERP system.
3. Seamless integrations
The tool must integrate with your existing systems. Look for pre-built connectors for common software like QuickBooks and SAP, and a flexible API and webhooks for custom systems.
4. Continuous learning and improvement
The best AI systems incorporate a "human-in-the-loop" learning mechanism. This means that any correction a user makes is used as training data to improve the model. The platform should get progressively smarter and more accurate over time, reducing the need for manual review.
5. Support agentic workflows
This is the most advanced evolution of IDP. Instead of a passive tool, an agentic platform is an autonomous system of specialized AI agents that collaborate to execute the entire business process. Here, a team of virtual agents handles the workflow. A Classification Agent sorts incoming documents, an Extraction Agent pulls the data, a Validation Agent performs tasks like three-way matching against purchase orders, an Approval Agent routes it to the right person, and a Posting Agent enters the final data into the ERP. The goal is to achieve a high Straight-Through Processing (STP) rate, where invoices flow from receipt to payment-readiness with zero human intervention.
A practical guide: Setting up your first automated invoice workflow
Getting started with automation can feel daunting, but it doesn't have to be. Here’s a more detailed look at how you can set up a powerful workflow in Nanonets.
Step 1: Choose your model
The first step is to select the right AI model. You can either use a pre-trained model or train a custom model. For invoices, our pre-trained model is the best place to start, as it has been trained on millions of diverse invoices and can recognize the most common fields right out of the box. The platform also intelligently identifies the document type—distinguishing an invoice from a purchase order—and routes it to the correct workflow.
Step 2: Set up your import channel
Next, you need to tell Nanonets how it will receive invoices. The most common method is to set up an automated email import. Nanonets provides a unique email address for each workflow that you can auto-forward invoices to, so they'll be processed automatically.
Step 3: Configure your data actions
Raw extracted data often needs refinement. This is where "data actions" come in. For example, you can add a "Date Formatter" action to automatically standardize all extracted dates to a single format required by your ERP system. For our client ACM Services, we set up an action to automatically look up a vendor's GL code from a master file and add it to the extracted data.
Step 4: Build your approval rules
This is where you embed your company's business logic. For example, you could build a two-stage approval:
- Stage 1 (PO Match): Use the "Match in Database" rule to check if the PO number on the invoice exists in your master list. If not, the invoice is automatically flagged for review.
- Stage 2 (Amount Threshold): Add a second rule that states if the invoice_amount is greater than $5,000, the invoice also requires approval from a finance manager.
Step 5: Configure your export
The final step is to get the clean, approved data into your system of record. You can configure the export to connect directly to your accounting software, like QuickBooks, and map the extracted fields to the corresponding fields in your system.
What truly sets a modern platform apart is its ability to handle your company's unique business rules. At Nanonets, we developed a feature called AI Agent Guidelines that allows you to give the AI broad, plain-English instructions to handle context-specific scenarios. For example:
- Vendor-specific logic: "If the vendor is XYZ, then the invoice_amount does not include taxes."
- Regional rules: "If an invoice is from Europe, the total_tax should include the sum of all VAT rates."
Don't just take our word for it: the proof is in the numbers
We’ve helped hundreds of companies transform their accounts payable processes. Here are just a few examples:
- Asian Paints, one of the largest paint companies in Asia, reduced its document processing time from 5 minutes to about 30 seconds, saving 192 person-hours every month.
- Suzano International automated the processing of purchase orders from over 70 customers, cutting the turnaround time from 8 minutes to just 48 seconds—a 90% reduction in time.
- Hometown Holdings, a property management firm, saved 4,160 employee hours annually and saw a $40,000 increase in Net Operating Income (NOI) after automating its property invoice management.
- Pro Partners Wealth, an accounting and wealth management firm, achieved a straight-through processing rate of over 80% and saved 40% in time compared to their previous OCR tool.
Final thoughts
The transition from manual invoice processing to an automated, AI-powered workflow is no longer a luxury—it's a strategic necessity. By leveraging AI to handle the tedious, error-prone task of data extraction, you free up your finance team to focus on higher-value activities like financial analysis and cash flow management.
Modern platforms like Nanonets provide the tools to not only extract data with incredible accuracy but to automate the entire end-to-end process. If you're ready to stop the paper chase and build a more efficient finance operation, it's time to explore what AI-powered automation can do for you.
Explore how this integrates into scalable AI workflows in our guide on - Automated Data Extraction for Enterprise AI.
FAQs
How is an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) platform different from a standard OCR tool?
A standard OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tool is just a digital transcriber that turns an image into raw text, often requiring rigid templates. In contrast, an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) platform like Nanonets is a complete solution that adds a layer of AI to understand the document's context, eliminating the need for templates. It also manages the entire end-to-end business process—including automated validation, multi-stage approvals, and seamless ERP integrations—all while learning from user corrections to become more accurate over time.
What kind of accuracy and Straight-Through Processing (STP) rates are realistic?
These are the two key metrics for measuring the success of an automation project. For accuracy, modern AI-based systems can achieve 95-98%, which is a significant leap from the 80-85% typical of older, template-based OCR. At Nanonets, we see this in practice with clients like ACM Services, who have achieved 98.9% extraction accuracy on their invoices.
For Straight-Through Processing (STP)—the percentage of invoices processed with zero human intervention—a good target for a well-implemented system is over 80%. This means 8 out of 10 invoices can flow directly from your email inbox to your ERP, ready for payment, without anyone on your team touching them. Our client Hometown Holdings, for example, achieved an 88% STP rate.
How does the system handle invoices in different languages and from different countries?
This is where a modern, AI-driven platform truly shines. Unlike template-based systems that require a new set of rules for every layout, an AI model learns the fundamental patterns of what an "invoice" is, regardless of the format.
- Handling different formats: The AI's ability to understand context and analyze the document's structure means it can adapt to different vendor layouts on the fly. This was a critical factor for our client Suzano International, who had to process documents in hundreds of different formats.
- Handling different languages: Advanced IDP platforms are trained on global datasets. The Nanonets platform, for example, can process documents in over 50 languages. Our work with JTI Ukraine, processing documents in Ukrainian, is a clear example of this global capability in action.
How is my sensitive financial data kept secure during this process?
Security for sensitive financial data is handled through a multi-layered approach. All data on a platform like Nanonets is protected with encryption both in transit (using TLS) and at rest. To ensure our processes meet the highest standards, our platform is compliant with certifications like SOC 2 and HIPAA, which are verified by independent audits. This is all built on secure, certified infrastructure, and your data is never used to train models for other customers. For organizations requiring maximum control, we also offer an on-premise deployment option via a Docker instance, ensuring no data ever leaves your own environment.
Can this technology automate other documents besides invoices?
Absolutely. While invoices are a primary use case, the underlying AI and workflow technology is designed to be document-agnostic. A key feature of the Nanonets platform is a Document Classification module that can automatically identify and route different document types to their unique workflows. Our client SafeRide Health, for example, uses this capability to process 16 different types of documents, including vehicle registrations and insurance forms, not just invoices. This same technology can be easily configured for other common business documents like purchase orders, receipts, and bills of lading.