What is intelligent document processing?
As we enter the sixth decade of the information age, data has become a currency of the business world. However, it is estimated that a vast majority of a company's data remains unstructured, taking the form of written text found in various forms such as reports, contracts, and emails.
The manual process of collating this information requires a significant amount of time and resources, ultimately underutilizing or burdening a company's most valuable asset - its human talent.
Intelligent document processing is increasingly being used in various industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, to automate many document-intensive tasks such as invoice processing, contract management, and compliance reporting among others.
IDP is also being used to extract insights from unstructured data in many documents, thereby adding to the strategic value of business operations.
According to Straits Research, the worldwide market for intelligent document processing was valued at more than $ 1 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach more than $ 6 billion by 2027.
Learn the impact of invoice reconciliation in the realm of intelligent automation by visiting What is Invoice Reconciliation?.
What is intelligent document processing?
Intelligent document processing (IDP) refers to the automation of data extraction from unstructured documents. It eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces errors, and increases efficiency in document management.
IDP or intelligent document processing is a software that automates the process of extracting, processing, and analyzing crucial document data for business operations. Such solutions are key to modernizing and streamlining the often outdated, manual, and slow processes associated with document processing.
The "intelligence" in intelligent document processing comes from the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools for data extraction. AI has the ability to process repetitive tasks without the cognitive limitations of humans; in fact, AI can produce more accurate results as it continues to process and learn.
How does IDP work?
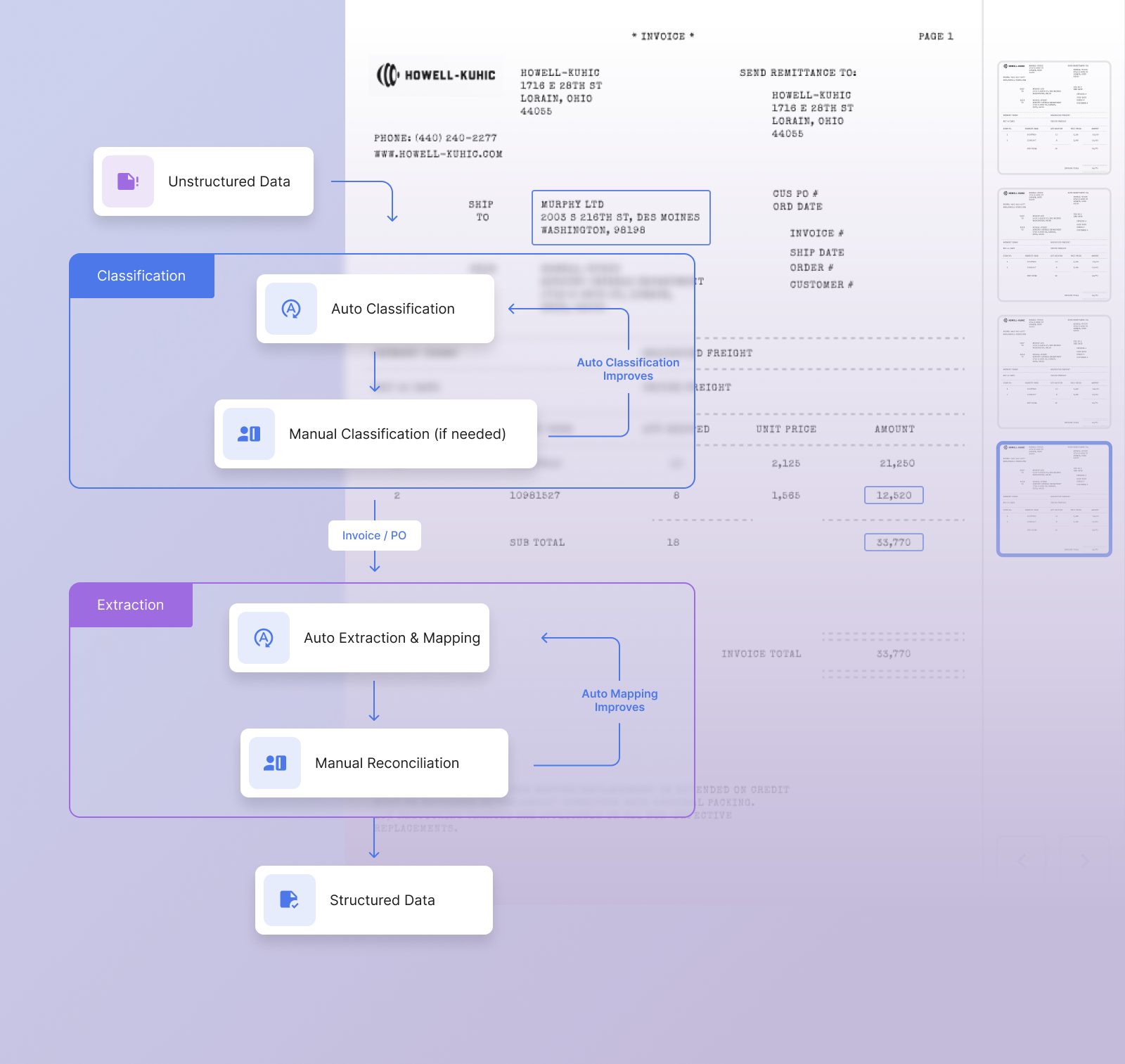
Intelligent document processing (IDP) typically involves a combination of optical character recognition (OCR), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) techniques to extract structured data from unstructured documents.
Here's a general overview of how IDP technology works:
- OCR is used to recognize and extract text from images or scanned documents, converting them into machine-readable text.
- The extracted text is then processed using NLP techniques to identify and extract relevant data such as names, addresses, dates, and numbers.
- Machine Learning algorithms are trained on a large dataset of labeled documents to recognize and extract specific information/fields from invoices, forms, or contracts.
- The structured data is then validated and cleaned, and any missing or incorrect data is corrected or flagged for manual review.
- The final output is a structured data format that can be easily integrated into other systems, such as databases or business intelligence tools, for further analysis and reporting.
IDP technology can learn and adapt to the specific requirements of different types of documents and industries, which makes it flexible and versatile. Intelligent document processing also allows handling large volumes of unstructured data, making it an efficient solution for automating data-intensive tasks such as invoice processing, contract management, and compliance reporting.
How does IDP differ from traditional document processing methods like Document Capture?
Document processing is aimed at transforming analog or unstructured documents into structured digital formats. It goes beyond mere scanning or photographing the documents but involves rendering documents and the data in them digitally comprehensible. Prior to the prevalent use of computer mice and scanners, data entry via keyboards was the norm. In the context of the "paperless office," an article from 1990 in The New York Times highlighted that document processing's starting point was the scanner. The journey of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) traces back to the late 19th century and continues evolving into 2022.
OCR's origins extend to 1914 when Emanuel Goldberg developed a machine capable of reading characters and converting them into telegraph code. Since then document processing automation has come a long way. Today, businesses dealing with data extraction from documents have three primary options: manual data extraction, OCR, and Intelligent Document Processing (IDP). The distinction between IDP and conventional document capture methods, like OCR, lies in their capabilities.
Where manual data extraction proves laborious and error-prone, OCR grapples with constraints tied to background colors, glare, and data structuring irregularities. OCR translates scanned images into machine-readable text, excelling with straightforward template-based documents but faltering when faced with layout or template deviations.
The subsequent evolution of OCR was template-based or zonal OCR, which recognizes designated text blocks for data extraction. However, zonal OCR's dependence on document templates impairs its adaptability and robustness. Its pitfalls include susceptibility to failure with minor template deviations and a limited contextual grasp of the extracted data.
Intelligent Document Processing overcomes these limitations. Representing the next generation in automated data extraction, IDP adeptly handles structured, semi-structured, and unstructured documents such as emails, PDFs, and diverse scanned files. Leveraging AI technologies like deep learning and machine learning, IDP achieves superior data extraction quality, even enhancing sub-standard scanned documents through noise reduction features. IDP's strength lies in its capacity to automatically categorize varied document types, extract data, and validate it against predefined rules, ensuring exceptional accuracy.
IDP solutions excel in their seamless integration potential with existing systems and automation platforms. With applications spanning claims processing, compliance in record management, and streamlined client onboarding, IDP's versatility fits across a spectrum of business functions. The divergence between IDP and conventional document processing methods not only underscores innovation and adaptability within the ever-evolving data management landscape.
IDP vs ADP
Automated document processing and intelligent document processing are related technologies but have distinct differences.
Automated document processing is used to convert paper documents into digital format, enabling them to be indexed and searchable in a database.
On the other hand, intelligent document processing not only digitizes and indexes paper documents but also extracts valuable information and provides insights from the data, taking document processing to the next level.
Here are some key differences between the two:
- Intelligent document processing uses advanced technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing, whereas automated document processing relies primarily on optical character recognition technology.
- Intelligent document processing is more sophisticated in its ability to understand complex/unstructured data, while automated document processing is more adept at plain old character recognition.
- Intelligent document processing can leverage AI & ML to learn and adapt to specific data extraction requirements and can produce more accurate results as it continues to process and learn. This isn't possible with automated document processing!
Benefits of intelligent document processing
The benefits of IDP are numerous and far-reaching, and businesses of all types and sizes are quickly realizing the value of this technology in streamlining their operations and improving their bottom line.
Here are some of the key benefits of intelligent document processing:
Increased Efficiency
Intelligent document processing eliminates the need for manual data entry, thus increasing the efficiency of business operations. This can lead to faster processing times, which can be especially beneficial for businesses that deal with high volumes of unstructured data.
Improved Accuracy
According to research, the probability of human error when manually entering data into simple spreadsheets is between 18% and 40%. In complex spreadsheets, that probability increases to 100%. IDP solutions are at least 95% accurate, and can eliminate serious errors associated with manual document processing.
Cost savings
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, intelligent document processing can significantly reduce labor costs. Additionally, IDP can help to reduce costs associated with errors and inaccuracies.
Better Decision Making
Intelligent document processing allows for the easy extraction of insights from unstructured data, making the process of decision making easier and more accurate. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that need to make data-driven decisions, such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Integration
Intelligent document processing can easily integrate with other systems, such as databases or business intelligence tools, for further analysis and reporting. This allows businesses to easily access and use the data that has been extracted, without having to manually feed it into another system.
Increase employee productivity
Intelligent document processing can improve both employee experience by eliminating the need for manual corrections, leading to faster approvals and reducing processing times. It also increases operational productivity by allowing valuable human resources to focus on more cognitive tasks instead of manual corrections.
Why should businesses use Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)?
Intelligent Document Processing solutions provide tangible benefits for businesses. From substantial cost savings and heightened data accuracy to increased employee productivity and novel capabilities, IDP is as a catalyst for streamlined operations and elevated decision-making. As companies embrace this technology, they position themselves to thrive in an environment characterized by efficiency, accuracy, and enhanced organizational dynamics. Some specific benefits include:
Lowering Document Processing Costs: The implementation of IDP software translates into tangible cost reductions for companies. Many users of IDP have experienced noteworthy savings, often amounting to thousands of work hours annually with just one application, such as invoice processing. These efficiency gains directly convert into substantial cost savings. Cost savings come from the elimination of errors in document data processing as well. Gartner reports that IDP and RPA tools can save finance departments alone can save 25,000 hours of rework caused by human errors at a cost of $878,000 per year for an organization with 40 full-time accounting staff.
Data Accuracy: IDP users circumvent the pitfalls of manual document data entry, sidestepping the multitude of errors typically associated with human input. Beyond mitigating these errors, this approach prevents potential issues stemming from inaccuracies, thereby safeguarding downstream business processes from disruptions. The accuracy achieved through IDP bolsters the foundation of reliable and precise data management.
Increased Employee Productivity: The implementation of intelligent document processing redefines employee roles by automating labor-intensive tasks that often rank low in terms of preference and value. By relieving employees of such repetitive work, organizations enable them to engage in more valuable tasks that contribute meaningfully to the organization's objectives. This not only bolsters departmental efficiency but also elevates overall employee morale, fostering a more motivated and engaged workforce.
Unlocking Brand-New Capabilities: For some users of intelligent document processing software, the efficiency achieved in electronic document processing has led to the creation of novel products for their customers. The streamlined and agile document processing has paved the way for innovative offerings that were previously unfeasible. Furthermore, IDP-equipped users gain access to richer, timely information, enabling better-informed decisions across the organization. This accelerated access to information translates into heightened decision-making prowess, underpinning strategic choices with reliable data insights.
Operational Efficiency and Enhanced Morale: Implementing IDP software fuels operational efficiency, not just within specific departments but organization-wide. The ripple effect of streamlined processes contributes to overall operational fluidity and effectiveness. Simultaneously, it boosts employee morale by liberating them from mundane tasks, fostering a more fulfilling work environment where they can concentrate on tasks that drive meaningful impact.
Intelligent document processing use cases
The use of intelligent document processing is not limited to a specific sector, it can be applied to various industries, and it can be used to automate many different types of tasks.
By automating data extraction tasks, processes can be expedited, both on an objective task-performance time scale as well as through the avoidance of errors that are commonly associated with manual data extraction processes.
The above applications of IDP make it a versatile and valuable technology for businesses of all types and sizes. Here are some examples of how different teams or organisations leverage intelligent document processing:
- Finance teams automate accounting, book keeping, loan processing, underwriting and accounts payable workflows among others.
- Healthcare organisations draw valuable insights from medical records, prescriptions, insurance claims, lab results, patient information forms etc.
- Insurance firms verify and analyse data from KYC documents, email attachments, transcripts, scanned agreements to process claims 80% faster.
- HR personnel improve candidate processing speeds by pulling contact information, education, work experience, skills and qualifications from CVs and importing the same into an ATS.
- Government agencies archive and verify government documents, tax returns, licenses, passports, permits and more.
- Retail and logistics firms automate procurement, supply chain, inventory management and logistics workflows that involve multiple documents such as invoices, receipts, bills of lading, packing slips etc.
- Law firms pull or archive information from complex contracts, agreements, regulatory filings and court orders.
- Real estate firms pull data from property titles, purchase agreements, lease agreements etc. into other business software.
How to choose the right IDP solution for your business?
When choosing an intelligent document processing solution, it is important to consider several factors to ensure that the solution meets the specific needs of your organization.
- To select an IDP that caters best to your organizational needs, the initial step is identifying your data processing requirements.
- In what format is the data received or stored (email, scanned document, physical paper etc.)?
- Is the data structured or unstructured?
- What is the volume of data you receive, and at what frequency, and how much of it do you really need to automate?
- After identifying your organization's initial data processing needs, the next step is to assess which data sets would be most appropriate for intelligent document processing. Documents that require the most amount of time to process manually are ideal for IDP.
- After identifying the datasets that would benefit most from intelligent document processing workflows, the next step is to select the IDP software. Here are a few key points to keep in mind while comparing intelligent document processing software:
- What is the expected accuracy level vs manual error rates? And can it be improved?
- Is the underlying IDP technology template-based or can it handle complex data formats that don't follow any prescribed structure?
- Can the IDP software read and understand all the types of data and documents that you currently deal with?
- Does the software readily integrate with your business tools of choice? If not, can that feature be customised for your use case?
- Can it handle your expected volume of data? And can it be scaled further?
- How long will the setup take? And what level of support can be expected?
- And finally compare competing quotes to get a better idea on pricing.
Steps in Implementing Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions
The implementation of IDP solutions involves a systematic approach, encompassing various stages to ensure successful integration and utilization. The following steps delineate a coherent process for organizations to adopt IDP effectively:
1. Assessment and Planning: Begin by evaluating your organization's data processing requirements. Determine the balance between structured and unstructured data and ascertain the most prevalent data formats. Assess the extent of automation desired in data processing. Identify workflows that would benefit most from automation. Document processing tasks consuming significant time are potential candidates for IDP adoption. Once these workflows are recognized, the focus shifts to selecting an appropriate IDP solution that aligns with the automation demand and organizational prerequisites.
2. Choosing the Right IDP Solution: Analyze the features, pros and cons of various IDP soltutions before choosing one that fits your needs. Assess the speed of implementation and ongoing maintenance requirements. Gauge the level of support provided by the software vendor, particularly concerning the intelligent document recognition technology. Ensure that the solution encompasses the ability to read all document types your organization handles. Additionally, assess whether the solution's accuracy significantly enhances error rates. User reviews can provide valuable information on what to expect with a particular tool.
3. Preparing the Data (Preprocessing, Classification, Extraction): The next step is to try out the IDP solution chosen. Data is essential for this step. Tools like OCR (Optical Character Recognition) that converts scanned images into machine-readable text can be used to convert unstructured data into semi structured digital forms. Techniques like binarization, deskewing, and noise removal refine OCR accuracy. Data extraction encompasses key-value pair and table extraction. Rule-based models and learning-based approaches leverage OCR's output for structured and semi-structured documents. Document classification identifies format, structure, and document type, paving the way for successful data extraction.
4. Data Validation: The accuracy and integrity of extracted data are paramount. IDP platforms employ external databases and pre-configured lexicons to validate extracted data. Discrepancies trigger flags for human review and correction, ensuring trustworthiness and reliability.
5. Training & Customizations: Advanced IDP solutions offer capabilities for custom ML model training for specific document types or domains. They leverage human verification outcomes to enhance ML model performance. Human input is integral for handling outliers, improving extraction quality, and refining preprocessing and classification.
6. Integration: Validated data is integrated into downstream applications like customer service platforms, data enrichment tools, and RPA solutions. These integrations drive decision-making and business process improvement, ultimately utilizing the data extracted and classified by the IDP solution.
7. Testing & Deployment: Before full-scale deployment, rigorous testing ensures the solution functions as intended across various document types and scenarios. After successful testing, deploy the IDP solution within your organization's operational framework.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: IDP implementation doesn't end with deployment. Regularly monitor the solution's performance, gather feedback, and fine-tune algorithms and models as needed. This iterative approach ensures the IDP solution remains aligned with evolving organizational needs and changing document processing dynamics.
Key Technologies in IDP
IDP encompasses a suite of cutting-edge technologies that work in harmony to convert unstructured data into structured, actionable information. These technologies bring efficiency, accuracy, and automation to document processing workflows. Some of the key components of IDP include:
1. Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Optical Character Recognition, or OCR, forms the bedrock of IDP. This technology empowers computers to transform various document types, including scanned papers, PDFs, and images, into editable and searchable content. OCR analyzes light and dark patterns within an image to discern characters, even accommodating diverse fonts and languages. In IDP, OCR acts as the initial step, converting text into a readable format for further processing. Despite its utility, OCR has limitations, such as susceptibility to image quality issues or intricate layouts. IDP systems address these by utilizing advanced techniques, including image preprocessing and machine learning to enhance OCR accuracy.
2. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) form the dynamic duo that drives IDP's data transformation and insights extraction. ML algorithms learn from training data, recognizing patterns in documents to improve extraction accuracy. Supervised and unsupervised learning methods play essential roles in classifying documents, extracting information, and validating data based on predefined rules. AI acts as the orchestrator, unifying OCR, ML, and other technologies into intelligent document processing systems. Notably, Natural Language Processing (NLP), a facet of AI, amplifies IDP's capabilities by enabling systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language, a crucial skill for handling unstructured data.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP takes center stage in IDP by combining computational linguistics with ML and deep learning models to comprehend human language intricacies. Its functions include:
- Text Extraction and Understanding: NLP extracts and interprets text from diverse document formats, accommodating paragraphs, bullet points, tables, and handwritten notes.
- Contextual Understanding: NLP gauges context, grasping nuanced meanings of words in different contexts to extract accurate information.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): NLP identifies and classifies named entities, such as people, organizations, and quantities, enhancing data point identification.
- Information Extraction (IE): NLP transforms unstructured text into structured data by extracting relationships between entities, sentiments, events, and facts.
- Text Classification and Categorization: NLP automates document classification based on content, employing techniques to sort documents into predefined categories.
- Error Detection and Correction: NLP detects and rectifies anomalies in extracted data, ensuring accuracy by contextual correction.
- Continuous Learning: NLP evolves over time through feedback, enhancing accuracy with each iteration.
4. Data extraction and data validation tools: Data extraction and validation tools encompass various solutions tailored to specific needs and sources. Common types include:
- Web Scraping Tools: Extract data from websites, simulating human behavior and handling diverse formats like HTML or XML. They gather text, images, links, tables, and structured data.
- Database Extraction Tools: Directly extract data from databases by executing queries or using connectors. Suitable for SQL-based (e.g., MySQL) or NoSQL databases (e.g., MongoDB).
- Document Extraction Tools: Extract data from documents like PDFs or Word files using OCR to convert scanned content into machine-readable text.
- Text Extraction Tools: Extract information from unstructured text sources (emails, social media) using NLP, text mining, and ML for sentiment analysis.
- Sentiment analysis aids decision-making, influencing strategies and product improvements, as seen in market research.
The technology stack in intelligent document processing encompasses a range of tools and technologies, each playing a distinct role in the workflow. Some core components include Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tools like Nanonets, Tesseract and Abbyy, Machine Learning frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch for model training and accuracy improvement, Natural Language Processing (NLP) libraries like NLTK and SpaCy to handle unstructured text, and Artificial Intelligence platforms like OpenAI and IBM Watson for adaptive learning. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools like UiPath and Blue Prism automate repetitive tasks, while Computer Vision tools like OpenCV aid in layout recognition. Cloud platforms such as AWS and APIs/SDKs like RESTful APIs facilitate integration, and databases like SQL and NoSQL store and manage the extracted data.
Nanonets for your IDP workflows
Nanonets is an intelligent document processing software that uses machine learning to automate all kinds of data extraction/processing workflows.
It utilizes a combination of OCR and deep learning algorithms to accurately extract data from various types of documents, such as invoices, receipts, bank statements, contracts and more.
Nanonets Intro
Nanonets offers several advantages as an IDP solution, such as its ability to handle a wide range of document types, its high level of accuracy, and its ease of use. With Nanonets, users can quickly and easily extract data from documents, which can save them a significant amount of time and effort.
Takeaway
Businesses that can effectively utilize cutting-edge technologies like IDP will have significant advantages in terms of efficiency and effectiveness. These technologies have the power to automate processes, reduce errors and increase efficiency. It's important to keep in mind that AI-based automation platforms are not magic solutions, they are the outcome of careful planning and collaboration between experts to solve real-world problems.
With the growing demand for automation and the increasing importance of data, IDP technology is poised to play a vital role in shaping the future of business. The time to invest in IDP is now, for those who do will be the ones who reap the benefits in the long run.



