The Invoice Validation Process
A recent survey entitled The e-invoicing Journey – 2019-2025, reports that on average 70 bills/invoices are currently exchanged per person, per day, all over the world. The invoice is, unsurprisingly, often referred to among accountants as the “queen of all documents” and is the most important document for accounting, taxation, and VAT activities. The importance of the invoice necessitates the correctness of data because any error in invoice data can have long-term consequences to the business in terms of its productivity, reliability, and relationships. This makes payables invoice validation a critical activity in the Accounts Payable (AP) function of any business.

Let us learn about invoice validation, its importance in the AP process and the benefits of invoice automation in the process.
Errors in invoices
Errors in invoices are not uncommon. They can arise from miscalculations, legislations, and, most commonly, human factors. A survey report titled “Lost in transaction 2020 – The hidden cost of invoice errors in the Nordics” that studied 1000 companies in Nordic countries showed that 0.53% of all invoices have errors in them. Assuming the generality of this number, and combining it with the earlier statistic of 70 invoices/person/day, it can be estimated that each person in the world, on average, is responsible for 139 faulty invoices every year.

An invoice contains critical data such as company IDs, tax information, service/product supplied, price, delivery status etc. Mistakes in invoices may be in the form of:
- Wrong name of the client
- Absence of clear itemization of products/services delivered/to be delivered
- Not in accordance with the purchase order
- Calculation errors
- Not using the right currency
- Not mentioning a due date
- Not mentioning discounts or penalty fees
- Tax rate errors
Invoice errors are serious problems because they can affect accounts receivables, inventory, and cash holdings by the company. Invoicing errors can affect the balance sheet amounts of a company, which can, in turn, affect its credibility and creditworthiness. Errors in paper-based invoices are expensive to fix – the rectification of invoice data can cost $53.50 per invoice on average.
Various surveys, such as the one by IACCM and Zen Enterprise have reported various factors that cause invoice errors.
- The scale of the business: While the scale of the business has nothing to do with the fraction of faulty invoices received or issued, the absolute numbers of erroneous bills would be small in a small business, which makes them easier to spot and tackle. As the business expands, the absolute number of invoices increases, which increases the number of faulty invoices as well, some of which may fall through the cracks and lead to problems in payments and accounting later.
- Nature of product/service involved: Invoice errors are more common in service than product delivery because the former inevitably involves various factors such as use rates, billable hours and differentiated charging levels. In goods delivery, variable discount arrangements and any form of ‘custom pricing’ could result in errors in invoice pricing. The granularity of pricing, driven by market segmentation can also increase the likelihood of incorrect billing.
- Human misunderstanding: The structure and wording of the contract or purchase order could be ambiguous, misleading, and misinterpreted, leading to wrong data in invoices.
- Disconnect: The lack of open and cohesive communication between the negotiators of the purchase and the implementing body, such as the accounts payable department can create downstream problems, especially in cases of non-standard prices or charges, which could lead to faulty invoices. A lack of clarity over roles and responsibilities for contract management could lead to poor information exchange that could lead to errors in billing.
- Absence of uniformity: Invoices are of varying formats. This leads to confusion in data extraction, especially when performed manually, or using rudimentary data-extraction tools, resulting in faulty data input and processing.
Looking to automate your manual AP Processes? Book a 30-min live demo to see how Nanonets can help your team implement end-to-end AP automation.
The invoice validation process
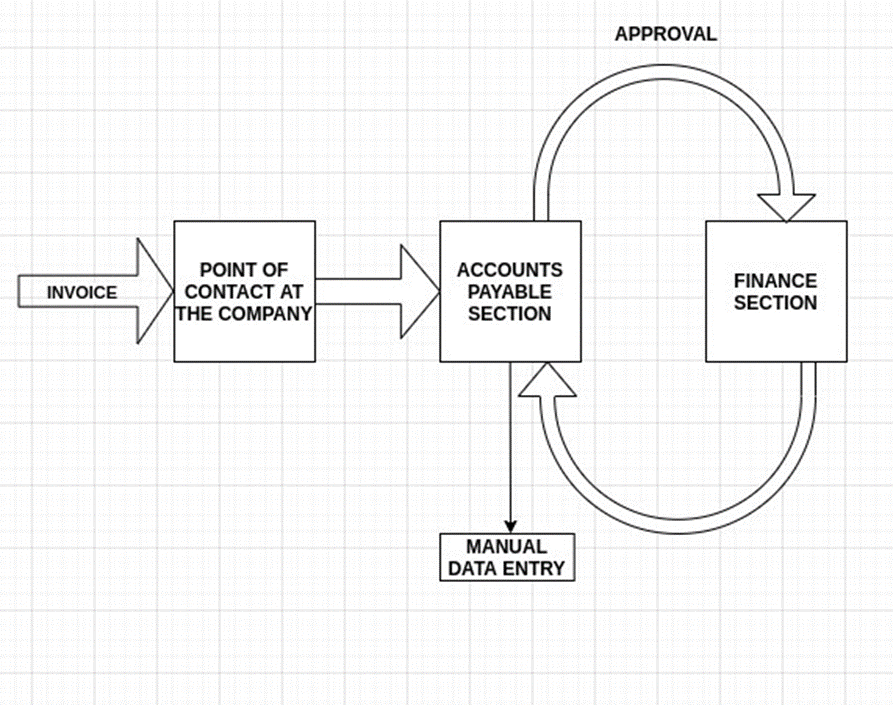
The validation of invoices is an important step in the invoice processing workflow in order to catch and rectify errors before payment is initiated. Some important payables invoice validation steps are:
- Categorization of the invoice: An invoice may or may not be issued in response to a formal purchase order. The categorization of the invoice into PO- or non-PO types is fundamental to determine further processing steps needed. PO-responsive invoices would entail two- or three-way matching processes and non-PO-invoices would require GL Coding & Approval routing.
- Name validation: The names of the vendors and the clients must be included correctly. This is required for accounting and tax purposes and for organized bookkeeping.
- Line-Item Validation: This seemingly onerous step involves checking all the details in the invoice, including reference numbers, quantity, quality, date, and delivery options and may involve cross-referencing data from multiple sources such as procurement records and receiving documents.
- Pricing validation: Simple calculation errors may lead to faulty totals and incorporation of taxation and freight/delivery charges could lead to mismatches in the billed amounts. Two- and three-way matching with POs and receipts is essential at this point to prevent errors in billing.
Set up touchless AP workflows and streamline the Accounts Payable process in seconds. Book a 30-min live demo now.
Problems of manual payables invoice validation
Manual validation of invoices becomes unwieldy and complicated, especially as a business expands. Some common problems associated with manual invoice validation are:
- Cost penalties: During validation, an error that is spotted is flagged as an exception and must be addressed by the accounts payable department. It has been shown that nearly a quarter of all invoices are flagged for exceptions that must be addressed by the accounts payable invoice processing personnel. This consumes inordinate amounts of time and results in invoice processing delays and affects payment schedules. Nearly 1 in 5 companies lose out on favorable terms and discounted rates due to delayed vendor payments.
- Not catching all errors: The mundanity and repetitiveness of the data validation activity could result in oversight problems. Not detecting and correcting errors in invoices can result in double payments, underpayments, delayed payments or missed payments, all of which can cost the company considerable money and time.
- Missed paperwork: In manual validation, the invoices may have to be moved physically from one person to the next, to check various fields, which can lead to misplacement and eventual loss of invoices. This could lead to problems in the accounting payable cycle, such as relationship issues with the vendor and delayed operations.
- Human effort wastage: Manually checking every line of the invoice and comparing them with the appropriate fields in other related documents is, understandably, time-consuming. Any time and effort spent on such cumbersome tasks are time and effort not spent on activities that are of value to the company.
- Delays in payments and other processes: A company, especially as it grows and expands, would receive multiple invoices from multiple vendors in the course of its business day. Given that 20% of invoices regularly contain incorrect or incomplete information, and a manual AP invoice approval workflow results in the AP department spending 25% of its time resolving issues and tracking down missing information. Such delays can snowball into delays in payment. According to Tally Street, 57% of payments in 2020 were collected late. Such late payments can seriously affect vendor-client relationships. For example, a 57% delay in payment could cost a vendor who has raised invoices worth $10 million, an immediate shortage of $5.7 million, an amount that is probably needed for the daily activities of the vendor’s business. This would naturally strain the relationship between the vendor and the client.
- Lack of transparency: It is difficult or even impossible to track the status of an invoice in its path of validation and approval, which makes backchecking and fore-planning difficult.
- Fraud vulnerability: Invoice fraud may be third-party fraud, labor mischarging, duplicate payments due to delays, or internal. A watertight validation process is essential to prevent fraud. Oversights in validation can result in fraud not being caught in time. Manual validation also carries with it complicity in the fraud, which can cost the company significantly not only in fiscal terms but also in morale.
Invoice validation software
Good invoice processing software can eliminate many of the problems associated with manual invoice validation. Invoice validation not only involves automatic capture of data from invoices and populating the appropriate fields of a database, but also matching the data with corresponding data from other documents involved in the purchase process. Accordingly, invoice validation software can perform 2-way, 3-way or 4-way matching depending on the needs of the organization. In 2-way matching, the invoice is automatically compared with the purchase order to ensure that what was asked for was what was delivered and billed for. In 3-way matching, the data in the invoice is matched with those from the PO and receipt documents. The most complex 4-way match includes inspection slips into the mix of documents to be compared and matched. Software tools can also be customized to match invoices to contracts.

The most rudimentary automation tool for invoice processing is the OCR data capture. Here, a combination of image capture hardware and conversion software convert invoices into ordered text that can be processed manually by the accounting team. It is obvious that this merely digitises the data and does not match them and must involve subsequent manual validations.
More comprehensive invoice validation tools can be of the following kinds:
- Robotic process automation (RPA) mimics human actions in repetitive tasks.
- Artificial intelligence (AI), computer science's "Holy Grail" in the words of Bill Gates, mimics human judgment and behaviour to match POs, invoices, and receipts. Machine learning (ML): ML is a subset of AI in which, the computer “learns from experience” through algorithms such as the Neural Network that mimic the learning process of the brain.
The above types of automated invoice processing tools can capture pertinent information from invoices, POs and other financial documentation and auto-process them in ways that mimic the human mind. The AI-enabled invoice processing, in particular, is better suited to compare and match records and make validation decisions such as passing the transaction, flagging errors, or raising exceptions. The AI algorithm performs can perform 2-, 3, or 4-way, depending on the needs of the company.
Book this 30-min live demo to make this the last time that you'll ever have to manually key in data from invoices or receipts into ERP software.
Advantages of invoice validation programs
Some specific advantages of invoice validation software include:
- Touchless invoice validation processing enabled by automation can eliminate paper-centric validation processes and minimise error-prone human intervention, thereby delivering better performance, scalability, and agility. Touchless processing often uses machine learning to train AIs to perform better than simple rules-based AI systems. The system, therefore, learns from both the vendor base and the specific intricacies of each vendor.
- Smart validation: Invoices can be matched through POs through the PO Number, Release, Line, Shipment and PO Receipt and sorted in various forms within seconds, a task that is herculean with human effort alone.
- Error flagging: Where the human brain can fail due to fatigue from repetitive action, automated systems, especially those based on ML can in fact, improve in performance with time and “experience”. Automation can ensure consistency of performance and enhance detection of small mistakes/errors that the human mind could miss before they cascade into larger ones. Timely error flagging can save time, reduce costly downtimes, and obviate serious firefighting at a later time.
- Increased Productivity: With freedom from time-consuming activities such as PO matching and invoice validation, the Accounts Payable team can now focus on human-centric activities such as financial planning, analysing, and deriving insights for improvements, and improving interpersonal and institutional relationships, all of which could improve the Bottom-Line.
- Data security and scalability: Greater operational efficiency results from automation’s ability to run 24X7, unlike human operators who are limited by mental bandwidth and geographic boundaries.
- Better vendor interactions: Automation of invoice validation can support automatic notification of vendors in case of failures and exceptions, which could allow them to correct the errors and resubmit without unnecessary delays.
- Audit Readiness: POs, GRNs, and invoices are among the most common documents asked during audits. AI-enabled PO matching already has these documents approved, matched, and organized, which enables a seamless audit process.
Invoice validation programs can help employees at various levels in the company’s hierarchy:
- Finance executives can reduce costs and free resources that can be reorganised to enhance the bottom line and assist in strategic and corporate growth.
- Corporate executives can better understand performance and monitor cash flow by analysis of the dashboard data offered by many of the financial automation software.
- The AP can eliminate paper invoices and manual interactions due to streamlined routing, coding, matching supplier invoices using pre-defined accounting rules.
- Accountants & Research Staff have complete and instant access to invoices for future planning.
Want to automate the Invoice Validation process? Check out Nanonets' pre-trained AI-OCR based Invoice Validation model or build your own customized Invoice OCR with Nanonets.
Nanonets for intelligent AP invoice validation
Nanonets is an AI-based software that can be used to automate and streamline AP invoice validation for your business. Data can be captured error-free from a variety of invoice file types. The AI engine of Nanonets can be trained with actual invoices, without the need for coding, which makes it customizable to the company. It also has built-in state-of-art algorithms and a strong infrastructure for multi-step validations. The Nanonets invoice processing software can be integrated with other systems such as the Mysql database, QuickBooks, or Salesforce and is platform agnostic. It is accurate and scalable, saves time and money for your Accounts Payable Invoice processing team and enhances productivity.
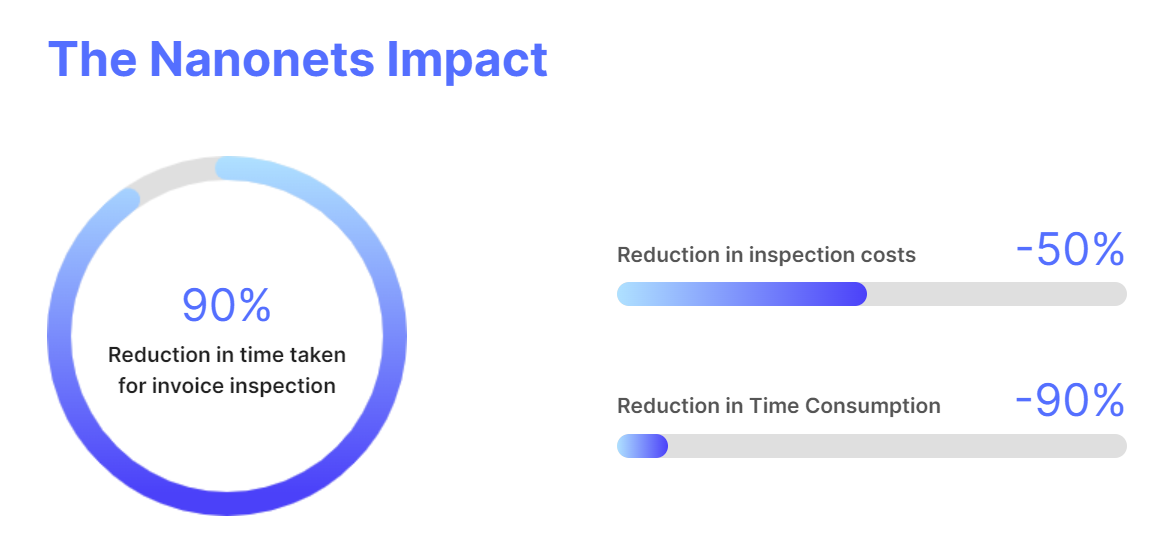
Takeaway
Automation of the invoice validation process can remove many of the hindrances associated with manual invoice processing and empower the accounts payable department to rapidly handle exceptions and errors, thereby avoiding costly delays in the procurement process. This can, in turn, lead to improved overall efficiency and profitability of the business.
Read More: The Guide to Invoice Audits



